Burning - Chemical Equations
Science Resource Description
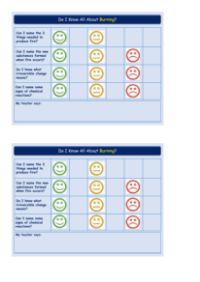
The process of burning various materials such as wax, paper, petrol, wood, coal, alcohol, gas, and oil involves a chemical reaction with oxygen. When these substances are ignited in the presence of oxygen, they undergo a combustion reaction. Combustion is a type of chemical reaction where a fuel reacts with oxygen to release energy in the form of heat and light. The general equation for the combustion of these materials can be represented as the fuel plus oxygen, resulting in the formation of carbon dioxide and water as the primary products.
Each of these materials—wax, paper, petrol, wood, coal, alcohol, gas, and oil—combines with oxygen in the air during the burning process to produce carbon dioxide and water. This reaction is common to many types of fuels and is an exothermic reaction, meaning it releases energy. The exact proportions of carbon dioxide and water produced can vary depending on the specific chemical composition of the fuel being burned and the conditions of the reaction, such as the availability of oxygen. Nevertheless, the products of complete combustion for these materials are universally carbon dioxide and water, indicating the conversion of the fuel's carbon content into carbon dioxide gas and the hydrogen content into water vapour.