Food - Presentation
Science Resource Description
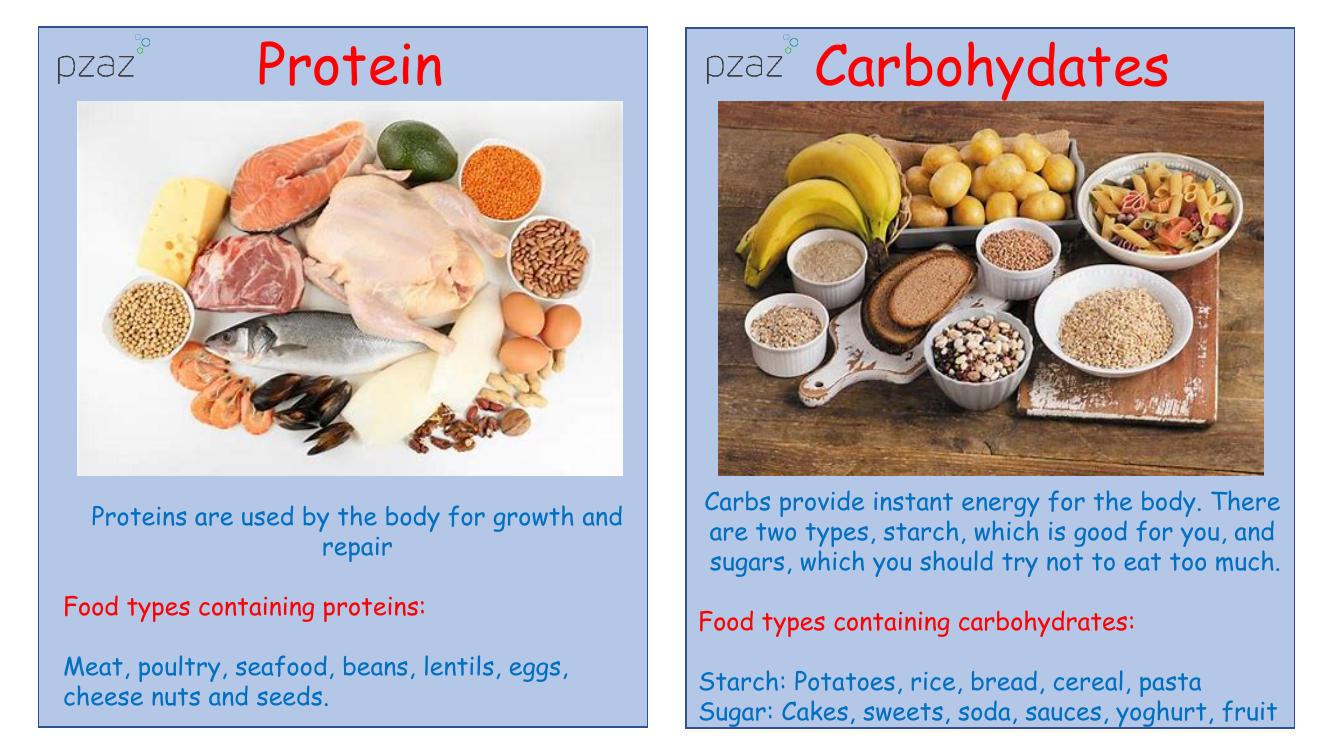
Proteins are essential nutrients that our bodies utilise for growth and repair. Various food sources are rich in proteins, including meat, poultry, seafood, beans, lentils, eggs, cheese, nuts, and seeds. Carbohydrates, commonly referred to as carbs, are the body's primary source of instant energy. They come in two main types: starches, which are beneficial to your health, and sugars, which should be consumed in moderation. Starchy foods include potatoes, rice, bread, cereal, and pasta. Sugary foods comprise cakes, sweets, soda, sauces, yoghurt, and fruit.
Fats are another crucial component of our diet, providing energy storage and insulation for the body. However, it's important to distinguish between saturated fats, which are generally considered unhealthy, and unsaturated fats, which are healthier choices. Saturated fats are found in butter, ghee, lard, coconut oil, and biscuits, while unsaturated fats are present in olive oil, sunflower oil, and avocados. Vitamins, of which there are 13 known types, are essential nutrients that help prevent disease and can be found in fruits, vegetables, meat, poultry, nuts, seeds, and mushrooms. Minerals, similar to vitamins, are vital for maintaining good health and are also found in these food groups. Fibre is necessary for digestive health, keeping food moving smoothly through the gut, with cereals, leafy greens, beans, and seeds being excellent sources. Although water is not a food group, it is essential for health, and it's recommended to drink eight glasses a day. It is naturally present in milk, fruits, and vegetables. A healthy diet is achieved by consuming the right amounts of each of the seven food groups, and overconsumption can lead to health issues.