Vocabulary - Multiplication and Division
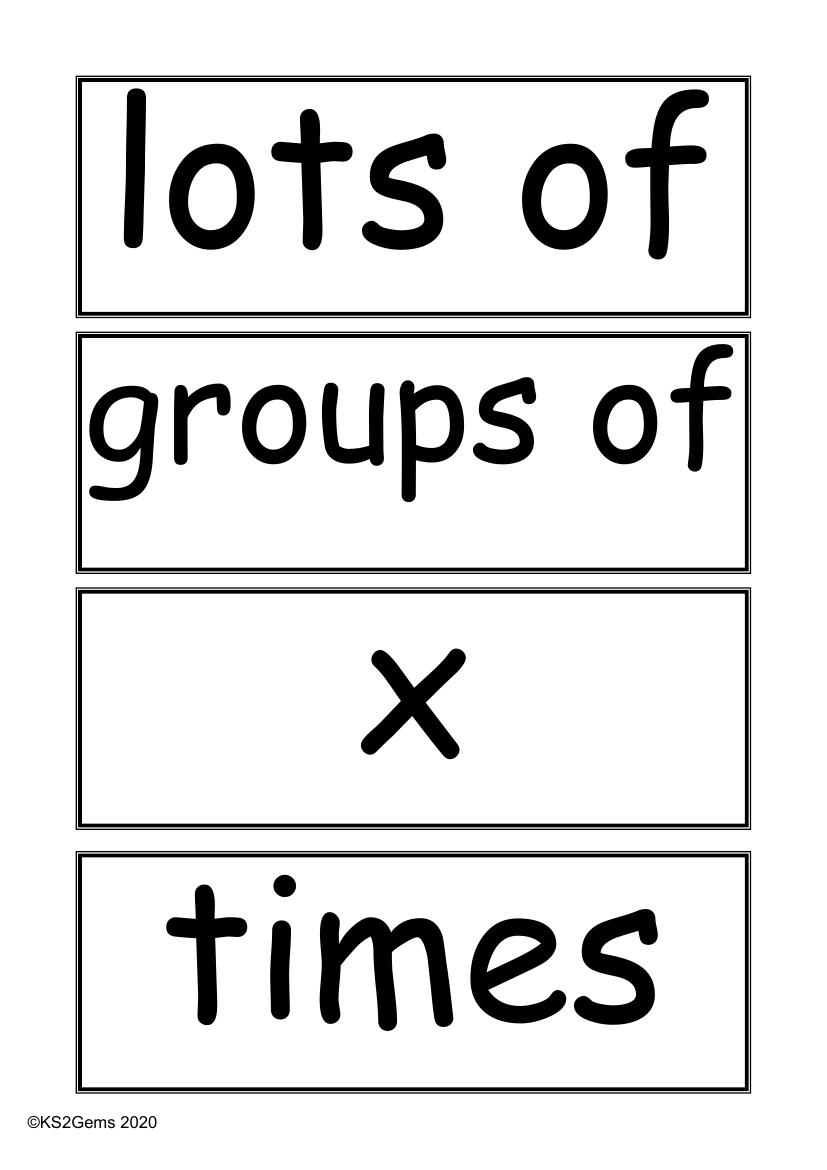
Maths Resource Description
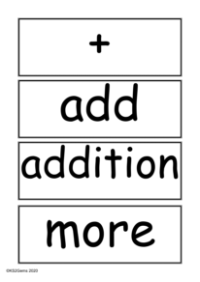
The vocabulary for multiplication and division is a fundamental part of mathematics education, particularly in Key Stage 2. Terms like "lots of" and "groups of" help students understand the concept of multiplication as repeated addition. The symbol 'x' stands for "times," indicating multiplication. For example, "five times six" is the same as "five groups of six." Students are taught to use words such as "multiply," "multiplication," and "multiplied by" to describe the action of calculating the total number of items in these groups. The term "multiple of" refers to a number that can be divided by another number without leaving a remainder.
The "product" is the result of multiplying numbers together. To "find the product" means to calculate the outcome of a multiplication operation. Multiplication can be expressed in terms like "once," "twice," "three times," and so on, up to "twelve times," to describe the number of times a number is to be multiplied. The concept of an "array" and understanding its rows and columns support the visualisation of multiplication. "Double" means to multiply by two, while "halve" means to divide by two. Division vocabulary includes terms like "share," "share equally," "one each," and "divide," which help students understand the process of dividing a number into equal parts. "Divided by" and "division" describe the action, while "remainder" refers to what is left over when a number cannot be divided exactly. An "equals" sign indicates that two expressions have the same value. The "quotient" is the result of division, and "divisible by" indicates that one number can be divided by another without a remainder. Understanding the "inverse operation" is crucial, as it relates to the relationship between multiplication and division. "Scaling" refers to multiplying or dividing a number to increase or decrease its size. Mathematical properties such as "commutative," "associative," and "distributive" describe rules that apply to these operations. Other important terms include "factor pairs," "common factors," "prime number," and "composite number," which are used to describe the relationships between numbers. "Short multiplication," "long multiplication," "short division," and "long division" refer to different methods of carrying out these operations. Finally, "common multiples," "order of operations," and "brackets" are used to describe more complex mathematical concepts and procedures.