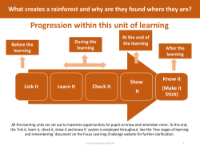
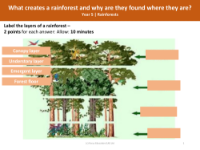
Three reasons - Why deforestation is bad for the environment

Geography Resource Description
Deforestation, the large-scale removal of trees from forests, has several detrimental effects on the environment. Firstly, it leads to a significant loss of biodiversity. Forests are home to a vast array of species, many of which are endemic and cannot survive outside their natural habitat. When trees are cleared, these species lose their homes and food sources, leading to a decline in wildlife populations and potentially causing extinctions. Secondly, deforestation contributes to climate change. Trees absorb carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, and help to regulate the Earth's temperature. When forests are cut down, not only is this carbon sink removed, but the stored carbon is also released into the atmosphere, exacerbating global warming.
Thirdly, deforestation disrupts the water cycle. Trees play a critical role in maintaining the water cycle by absorbing and releasing water vapor through their leaves in a process known as transpiration. This contributes to the formation of clouds and precipitation. The removal of trees can lead to a drier climate and disrupt rainfall patterns, which can have far-reaching effects on agriculture and water supplies. In addition to these points, deforestation can also lead to soil erosion and degradation, as tree roots that hold soil in place are removed, and the protective canopy that prevents heavy rainfall from directly hitting the soil is lost, making it more susceptible to erosion.