Merits and drawbacks of glass - Worksheet

Science Resource Description
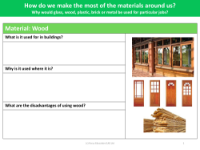
When considering the use of glass in building construction, it's important to examine both its merits and drawbacks. Glass is commonly used in buildings for windows, doors, and sometimes even walls. The material is chosen for its transparency, allowing natural light to enter indoor spaces and providing occupants with outside views. This can enhance the aesthetic appeal of a building and reduce the need for artificial lighting during the day. Moreover, glass can be treated or combined with other materials to improve its insulation properties, contributing to energy efficiency in temperature regulation.
However, there are also disadvantages associated with the use of glass in construction. One of the main concerns is its fragility; glass is more prone to breakage than many other building materials, which can pose safety risks and require careful handling and maintenance. Additionally, if not properly insulated, glass can lead to significant heat loss in colder climates or heat gain in warmer climates, impacting the building's energy consumption. To make the most of materials like glass, wood, plastic, brick, or metal, architects and builders must consider the specific properties of each and choose them based on the functional requirements of the job, such as strength, durability, insulation, and aesthetics. The selection process often involves balancing the benefits of a material against its limitations to achieve the desired outcome for the building project.