Habitats - Keywords
Science Resource Description
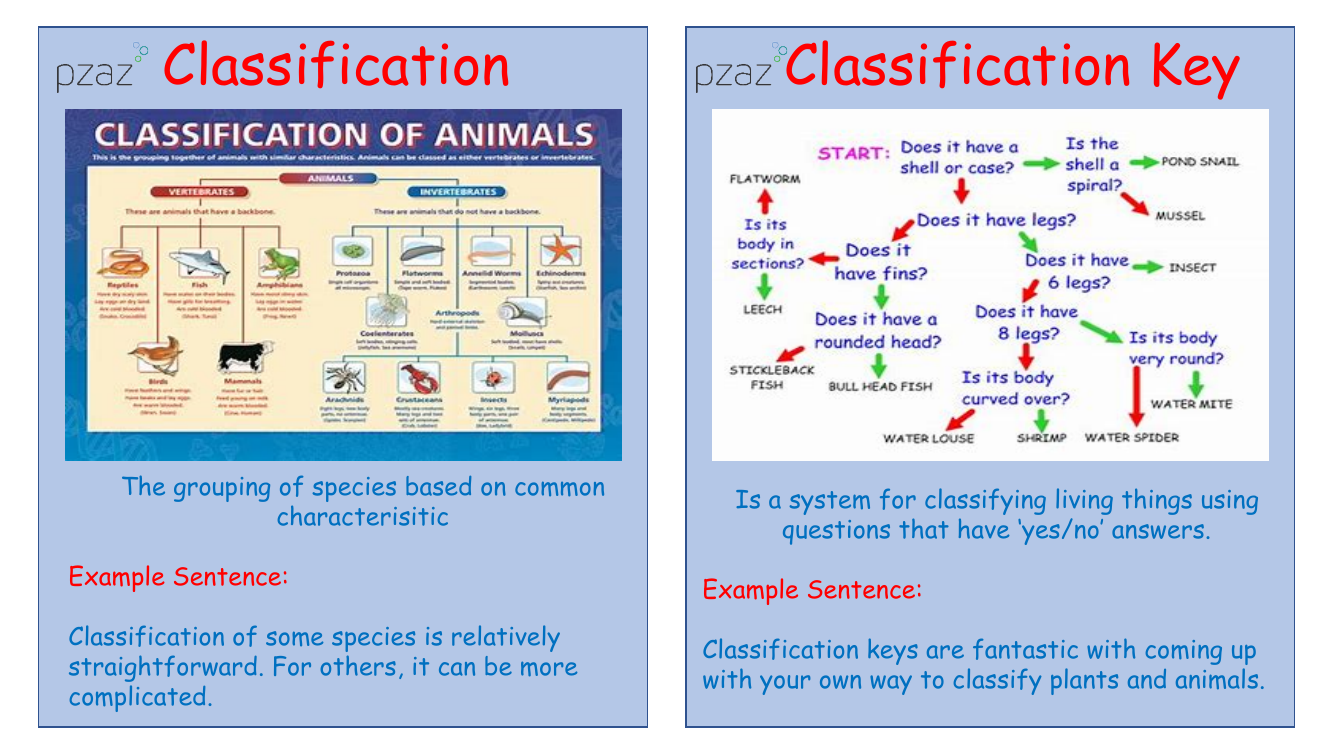
In the study of habitats, 'classification' is an essential concept, referring to the method of grouping species based on common characteristics. This process can range from straightforward to complex, depending on the species in question. To aid in classification, a 'classification key' is used, which is a system that employs a series of 'yes/no' questions to systematically identify living things. This tool allows for a structured approach to distinguishing between various plants and animals.
Another significant term is 'human impact,' which encompasses the influence humans have on the natural environment, including both beneficial and detrimental effects. For instance, the creation of nature reserves is an example of a positive human impact, while the negative consequences of actions like deforestation are profound, leading to species extinction. The 'environment' refers to the conditions and surroundings where plants and animals live, and within these environments, specific 'habitats' are the places where particular organisms are found, such as aquatic or terrestrial locations. Additionally, 'migration' is the term for the seasonal journey animals undertake between habitats, which can be perilous, as seen with the Wildebeest's dangerous crossing of the Zambeze river. Some animals 'hibernate' to survive the winter, entering a state of dormancy. Lastly, a species is considered 'extinct' when there are no surviving individuals left, as was the fate of the dinosaurs after a catastrophic meteor impact altered their habitat irreversibly.