Evolution - Keywords
Science Resource Description
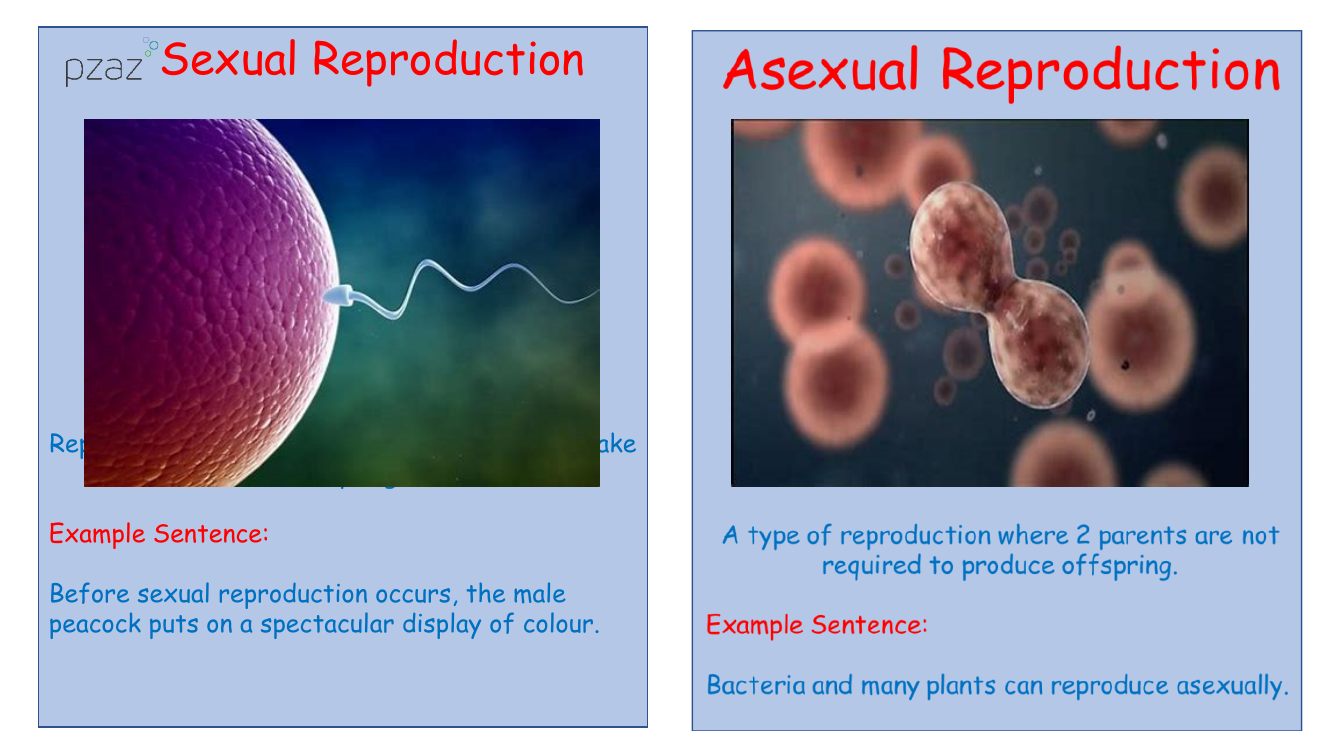
Sexual reproduction is a biological process requiring two parents to produce offspring. An example of this can be seen in the animal kingdom where, prior to mating, a male peacock will exhibit a vibrant and colourful display to attract a mate. In contrast, asexual reproduction does not require two parents; offspring are exact genetic replicas of the single parent. This method is common in bacteria and many plant species. The term 'offspring' refers to the young produced as a result of reproduction in both plants and animals, such as a wolf litter averaging five pups.
Reproduction is the overarching term for the mechanism through which living organisms produce new individuals. For instance, male buffalo engage in head-to-head combat as part of their mating rituals. The concept of variation highlights the differences between individuals within a species, like the range of heights found in humans. A characteristic is a distinctive feature of an organism, such as the giant squid's exceptionally large eyes. Adaptation is the evolutionary process by which species become better suited to their environment, exemplified by the giraffe's elongated neck. The environment is the natural home or conditions in which an organism lives, like the nutrient-poor habitat of the Venus Fly Trap. Traits that are inherited are passed down from one generation to the next, such as eye colour in humans. Evolution describes the gradual change in inherited characteristics over generations, which can be observed in the fossil record of horses. A species is a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring, and there are approximately one million known plant species. Lastly, fossils are the preserved impressions or remains of ancient organisms, often found embedded in rock, and can be seen in museums around the world.