Animals - Keywords
Science Resource Description
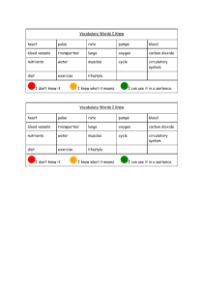
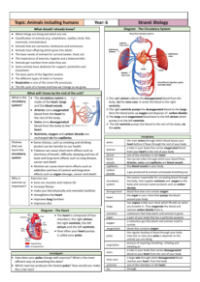
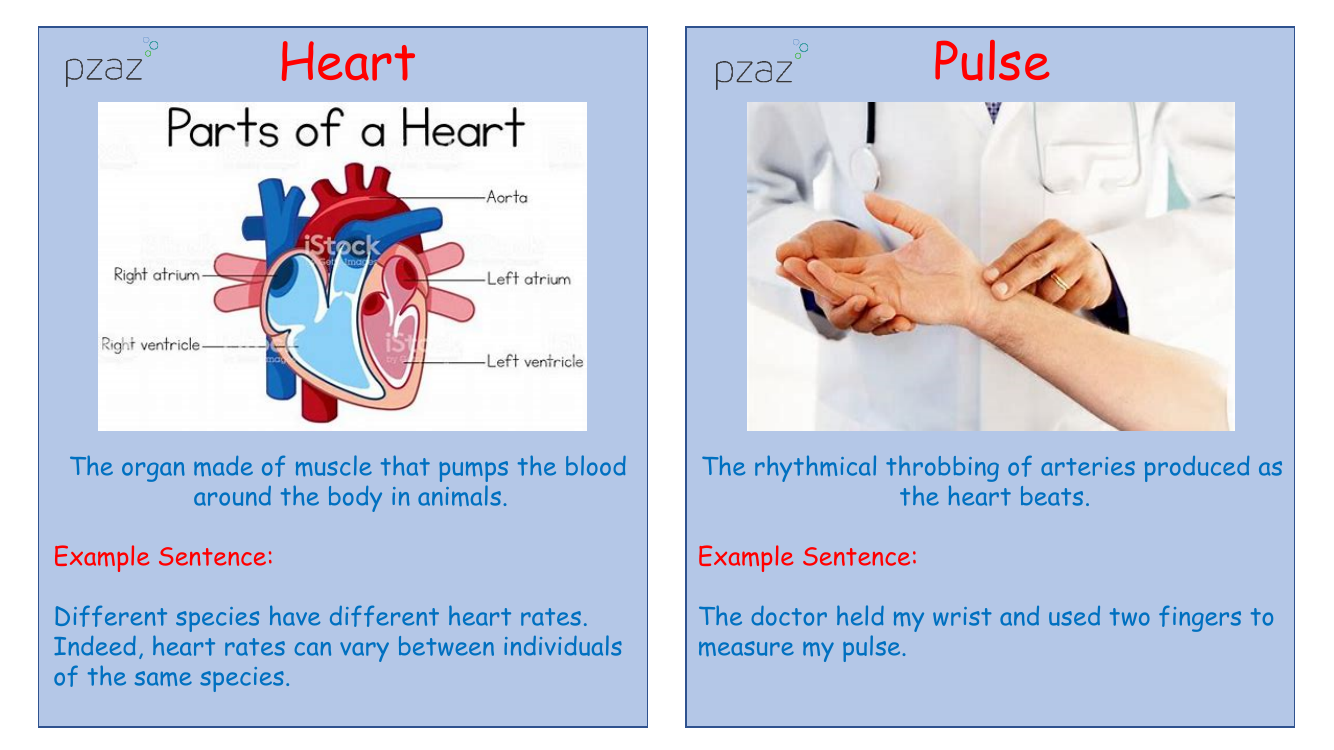
The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout an animal's body. It is a crucial component of the circulatory system, and heart rates can significantly vary not only across different species but also among individuals within the same species. The pulse, on the other hand, is the rhythmic throbbing felt in the arteries each time the heart beats, and it is commonly measured by doctors to assess the heart's rhythm and strength.
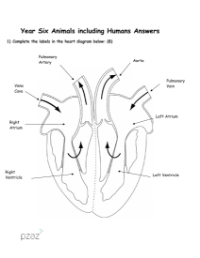
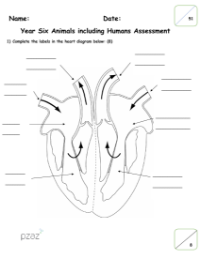
Blood is a vital fluid that transports oxygen and nutrients to every part of an animal's body while also carrying away waste products for disposal. Contrary to some beliefs, blood is never blue; it is always red, though the shade can vary depending on oxygenation. Blood vessels are the conduits through which blood travels, with arteries and veins being the main types. Arteries, characterized by their thick walls, carry blood away from the heart, while veins, with thinner walls, return blood to the heart. The aorta is the principal artery exiting the heart, and the vena cava is the main vein bringing deoxygenated blood back to it. The heart itself comprises ventricles and atria, the larger lower chambers and the upper chambers, respectively, with the left ventricle having the thickest wall to pump blood the furthest distance. Valves within the heart ensure blood flows in the correct direction. Oxygenated blood refers to blood rich in oxygen, typically carried in arteries, while deoxygenated blood, lacking oxygen, is found in veins. The terms also reflect the body's respiratory process, where oxygen is inhaled and carbon dioxide, a waste product, is exhaled. Nutrients are essential substances required by cells for growth and health, and together with oxygen, are delivered through the circulatory system, which boasts an extensive network of blood vessels. Lifestyle factors, including diet, drug use, and exercise, can significantly impact the health and efficiency of the circulatory system.