Space - Keywords
Science Resource Description
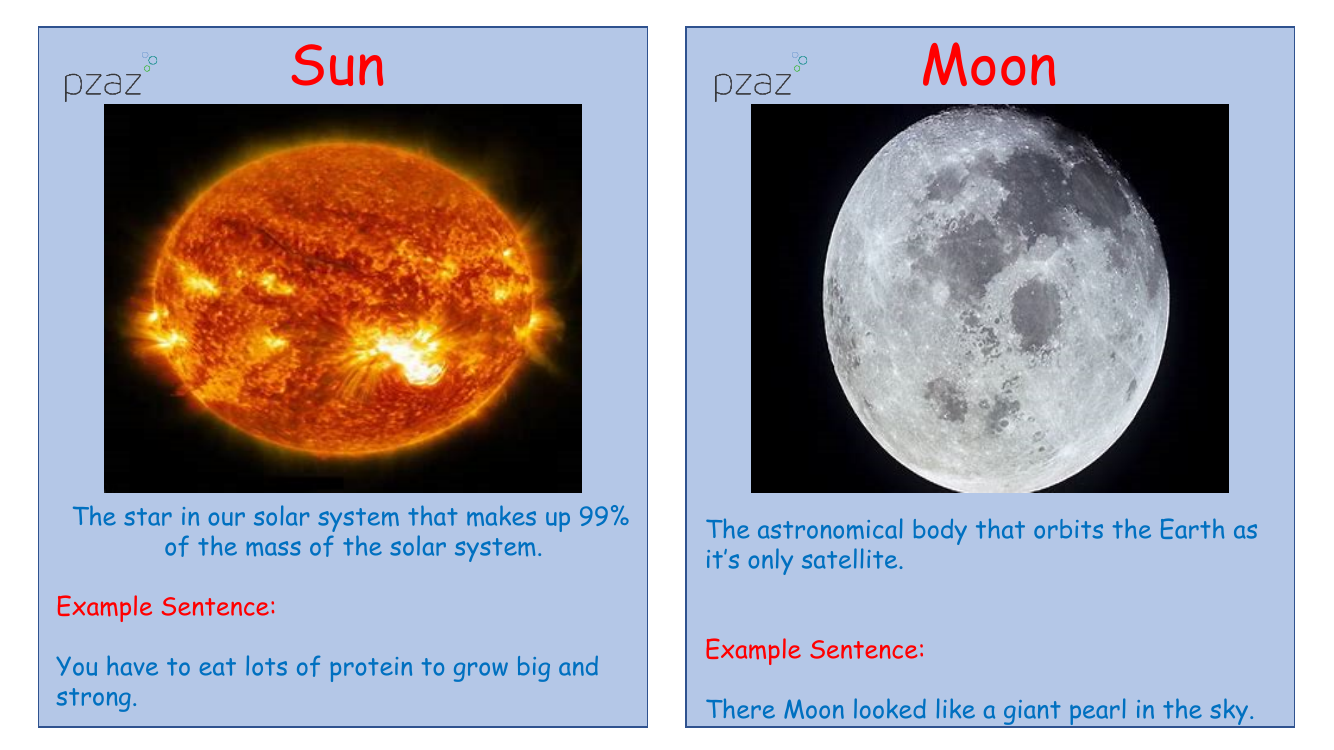
The Sun, the powerhouse of our solar system, is a star that holds a staggering 99% of the system's mass, illuminating and energizing the planets that orbit it. Like how a balanced diet with ample protein is essential for growth, the Sun is vital for the sustenance of our solar system. In contrast, the Moon, Earth's sole natural satellite, gracefully orbits our planet, often compared to a radiant pearl adorning the night sky. This celestial dance between Earth and Moon has been a source of wonder for eons.
Mercury, the solar system's smallest member and the nearest neighbour to the Sun, zips around our star in a swift 88 Earth days, marking its year. Following Mercury is Venus, Earth's cosmic twin in size but unparalleled in heat, with a thick cloud cover that ensnares solar warmth. Our home, Earth, is the oasis of life and the fifth largest planet, uniquely supporting a myriad of living organisms. Mars, known as the Red Planet, is roughly half Earth's size and has inspired tales of interplanetary invasion, notably in H.G. Wells's 'War of the Worlds'. Beyond Mars, we find Jupiter, a gas giant so massive it nearly became a star, and Saturn, the ringed beauty that could hypothetically float in water due to its low density. Uranus and Neptune, the solar system's distant giants, stand out with their immense sizes, with Neptune named after the Roman god of the sea, marking the edge of the planetary lineup.
When discussing celestial bodies, terms like 'spherical' and 'elliptical' describe their shapes, with planets being nearly spherical, slightly flattened due to their rotation, and orbiting the Sun in elliptical paths, as discovered by Johannes Kepler. The concept of rotation explains the daily spin of Earth, creating our day and night cycle. Orbits are the paths celestial bodies follow, such as the Moon's elliptical journey around Earth. The directional terms 'clockwise' and 'anticlockwise' help us understand the rotational direction, with Venus uniquely spinning clockwise, while the standard movement for planetary orbits around the Sun is anticlockwise.