Nutrition - Food Types Cards
Science Resource Description
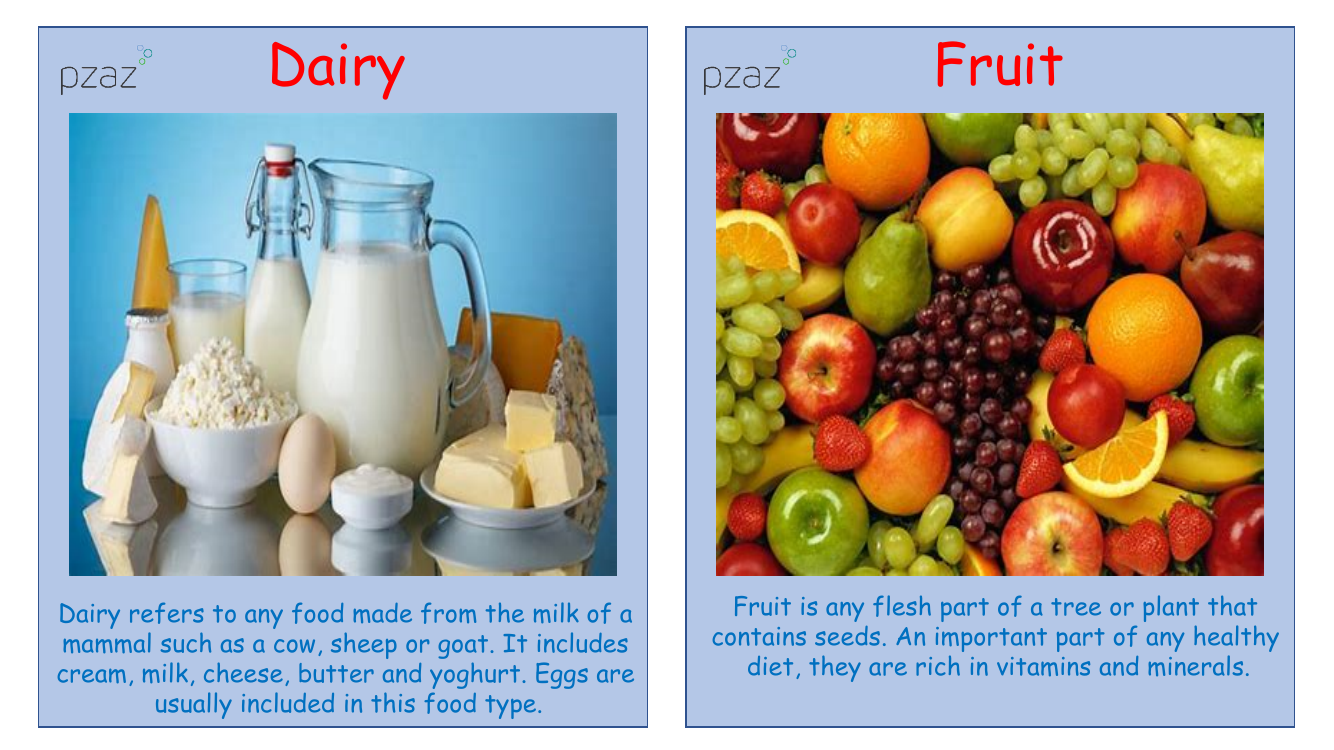
Dairy products are derived from the milk of mammals like cows, sheep, and goats. This category encompasses a variety of items including cream, milk, cheese, butter, and yoghurt. Contrary to common belief, eggs are typically categorised alongside dairy foods. These products are essential for providing calcium and other vital nutrients, though they vary in fat content and nutritional value.
Fruits are the seed-bearing parts of plants, usually the fleshy sections that grow on trees and other plants. They are an integral component of a balanced diet, packed with essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall health. Similarly, vegetables are also nutrient powerhouses, loaded with vitamins, minerals, and dietary fibre, and are recommended to be included in every meal for optimal nutrition. Meat, from animals such as cattle, pigs, and sheep, is a key source of protein and can contain varying levels of fat. It also includes offal, which are the organs of these animals, and is consumed globally. Poultry refers to bird meat, like chicken and turkey, known for its high protein and lower fat content. Fish, such as cod and tuna, provide protein and beneficial fats and are advised to be eaten regularly, ideally twice a week. Seafood, which includes prawns and oysters, is harvested from aquatic environments and offers high protein and minerals with low carbohydrate content. Pulses, including peas, beans, and lentils, are plant-based foods that are rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins, making them a staple in many diets. Nuts and seeds are compact sources of protein, fibre, and numerous vitamins, often referred to as superfoods due to their dense nutritional profile. Lastly, cereals are grains from crops like rice and wheat, providing a good source of fibre, vitamins, and minerals, and are a fundamental part of many diets worldwide.








