What causes an earthquake?

Geography Resource Description
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. This release of energy usually occurs because of the movement of tectonic plates, which are massive sections of the Earth's crust that float on the semi-fluid layer beneath them. These plates constantly move, but they can become locked due to friction. When the stress on the edge overcomes the friction, there is an earthquake that releases energy in waves that travel through the Earth's crust and cause the shaking that we feel. During an earthquake, the initial jolt is often followed by smaller tremors known as aftershocks. These aftershocks occur as the strata, or layers of rock, adjust to the new positions after the slip.
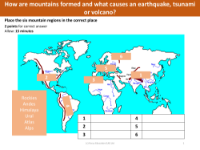
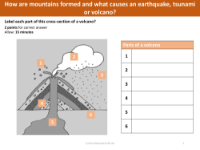
Mountains are formed through a process called orogeny, which is primarily the result of tectonic plate movements. When plates collide, they can push the Earth's crust upward, forming mountain ranges. Earthquakes can be associated with such tectonic processes, especially in mountainous regions. Tsunamis are typically caused by undersea earthquakes that displace large amounts of water, leading to powerful and long-reaching waves. Volcanic activity can also be related to the movement of tectonic plates, particularly when one plate is forced under another, melting rock and resulting in volcanic eruptions.