Give me 3 - Electricity
Science Resource Description
Electricity is a fundamental form of energy observable in positive and negative forms that occurs naturally (as in lightning) or is produced (as in generator) and that is expressed in terms of the movement and interaction of electrons. It is crucial in our daily lives as it powers most of our modern conveniences, from lighting and heating to powering appliances and electronic devices that we rely on for work, leisure, and communication. The importance of electricity extends beyond mere convenience; it is integral to the functioning of hospitals, transportation systems, and the vast majority of industrial processes. Its availability and reliability are critical for the economic development and the quality of life in modern society.
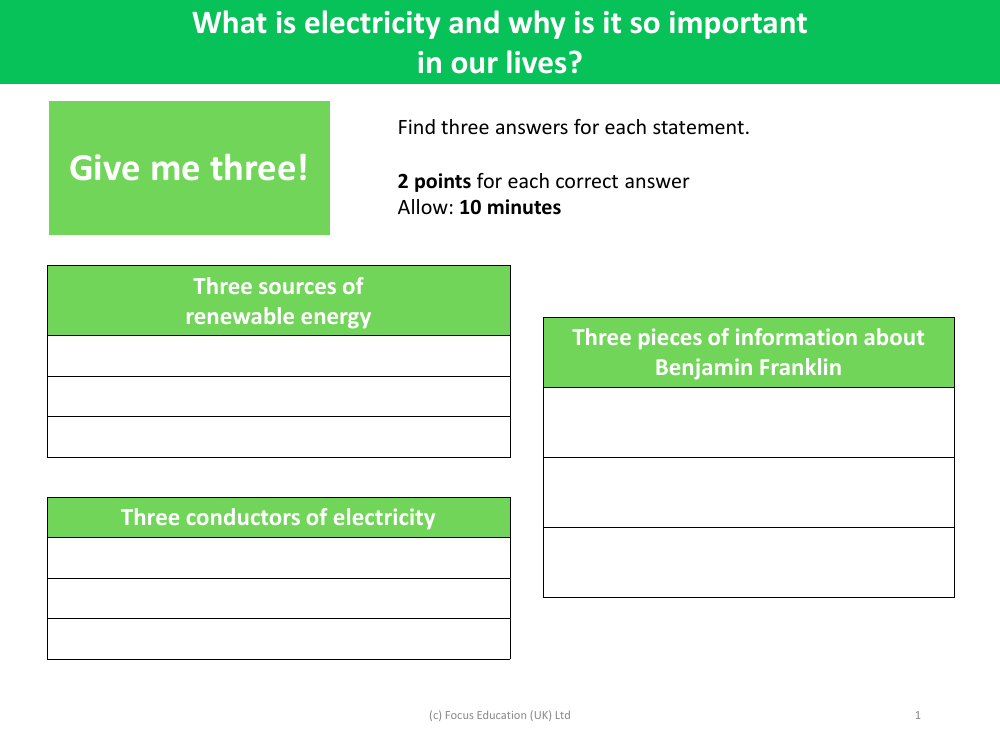
Benjamin Franklin is one of the most celebrated figures in the history of electricity. He is renowned for his experiments with electricity, most famously the kite experiment which demonstrated that lightning is a form of electrical discharge. Franklin also invented the lightning rod, a device that protects buildings and ships from lightning damage by directing the charge harmlessly into the ground. Additionally, he coined a number of terms used in electricity today, including 'battery', 'conductor', and 'electrician', and his studies laid the groundwork for the understanding of electrical conduction and insulation.
Conductors of electricity are materials that allow electric charge to flow through them with relative ease. Three common conductors are copper, which is widely used in electrical wiring and electronics due to its high conductivity and ductility; aluminum, which is used for overhead power lines and in power distribution systems because it is lightweight and also conducts electricity well; and silver, which has the highest electrical conductivity of all metals but due to its cost, it is used more selectively in specialised equipment and in situations where high conductivity is particularly required.
Renewable energy sources are those that can be replenished naturally and are considered environmentally friendly alternatives to fossil fuels. Three popular sources of renewable energy include solar energy, harnessed using solar panels to convert sunlight directly into electricity; wind energy, captured by wind turbines that convert the kinetic energy of wind into electrical power; and hydropower, generated by using the movement of water through turbines to produce electricity, typically in large dams or through smaller scale hydroelectric systems.