Sound - Keywords
Science Resource Description
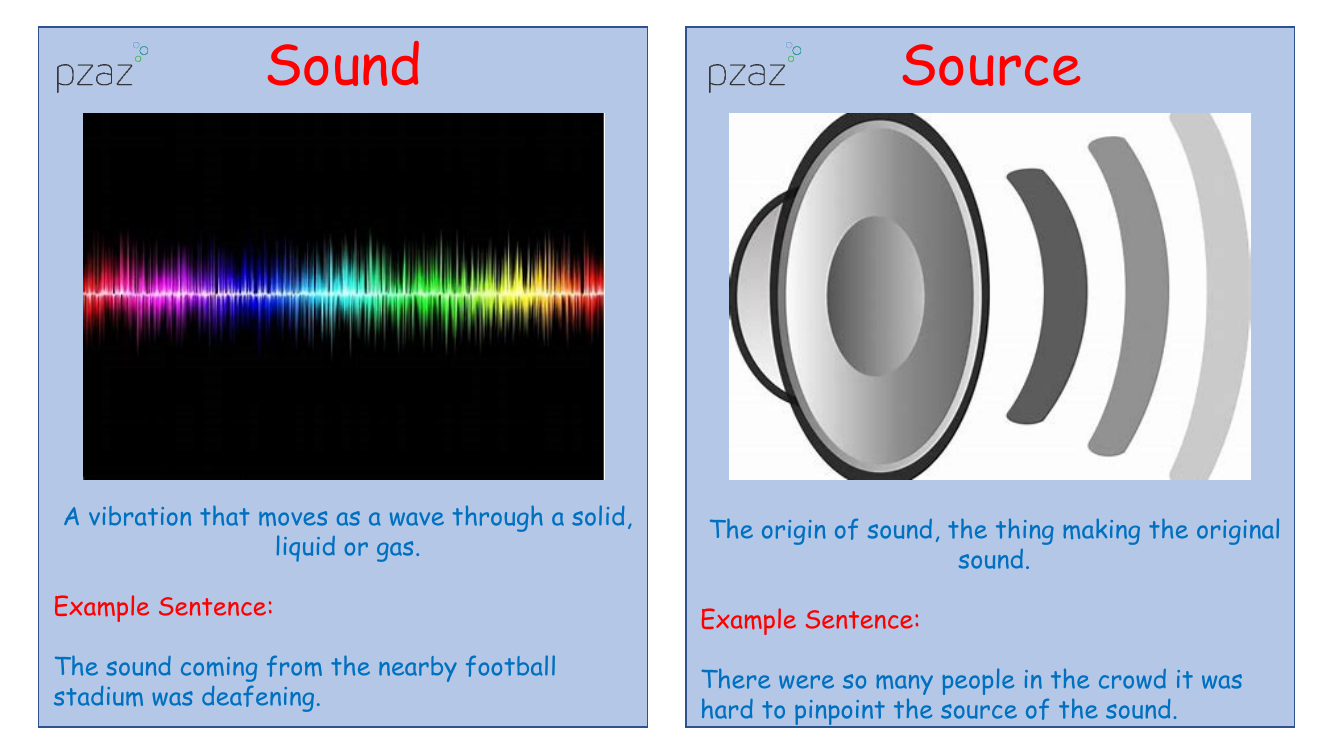
Sound is a phenomenon resulting from vibrations that travel through different mediums such as solids, liquids, or gases in the form of waves. This can be experienced in various ways, for example, the overwhelming noise emanating from a football stadium. The source of a sound is the originator of the noise, like identifying the specific person cheering in a bustling crowd, which can often be challenging due to the multitude of concurrent sounds.
The process of creating sound involves vibration, where an object moves back and forth around a central point, such as a tuning fork that is struck to produce a pure tone. These vibrations occur at different frequencies, measured in Hertz (Hz), determining the pitch of the sound—whether it's high and 'squeaky' or low and deep. The volume of sound refers to its loudness, with our daily lives filled with varying volumes, from the blaring music that prompts a parent's complaint to the soft rustle of leaves barely audible to our ears. Sound can be loud, causing a lingering ring in the ears post-concert, or faint, barely perceptible in the background. Insulation materials can absorb sound waves to prevent them from travelling, offering protection in noisy environments. Sound travels differently through the three states of matter, with solids conducting sound waves more efficiently due to closely packed particles, whereas gases are less effective as the particles are more dispersed. The distance sound travels can cause the sound waves to dissipate or spread out, reducing the intensity of the sound as it moves further from its source.