Rocks - Keywords
Science Resource Description
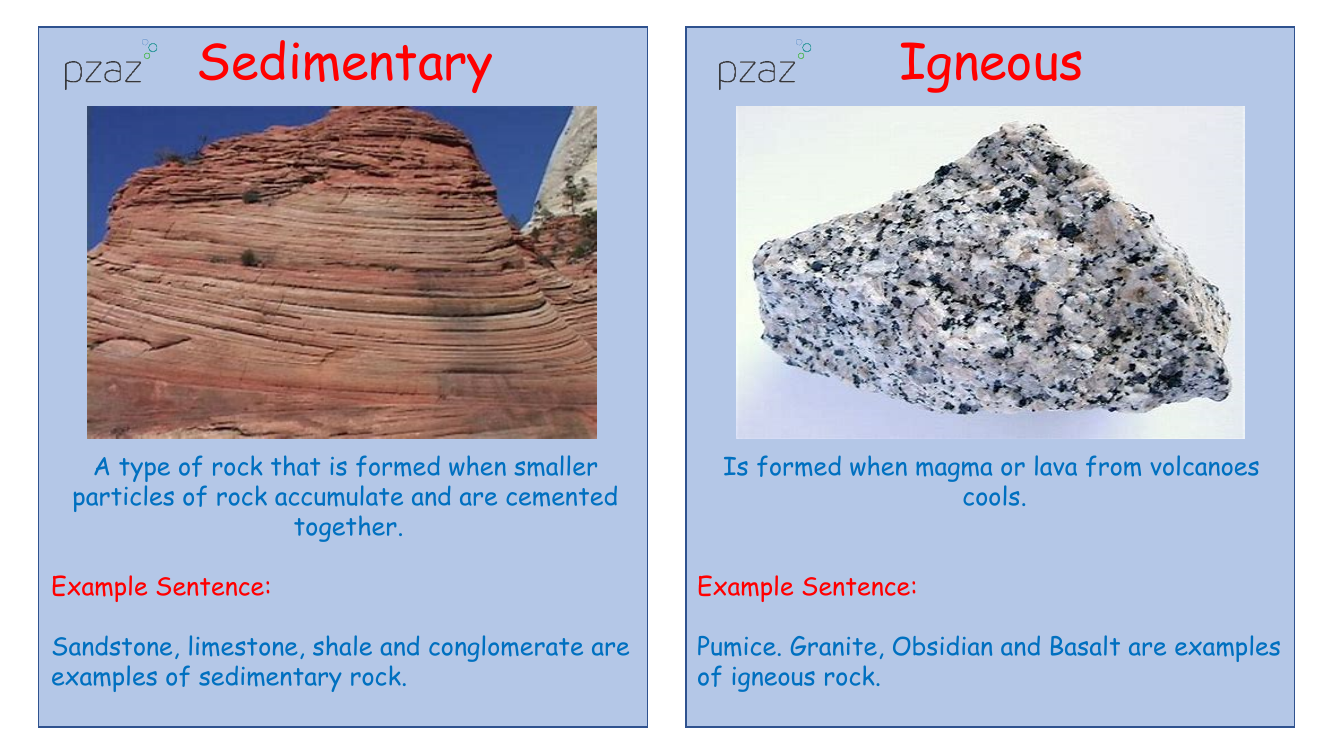
Sedimentary rocks are formed through the accumulation and cementing of smaller rock particles. These rocks are known for their origins in environments where sediments can deposit and lithify over time. An example of sedimentary rock includes sandstone, which, along with limestone, shale, and conglomerate, is created through this natural geological process.
Igneous rocks, on the other hand, originate from the cooling of magma or lava that erupts from volcanoes. These rocks are classified by their formation process and can be either intrusive or extrusive, depending on whether they cool within the Earth or on the surface. Examples of igneous rocks include pumice, granite, obsidian, and basalt. Metamorphic rocks such as gneiss, slate, marble, and schist are the result of the transformation of igneous or sedimentary rocks under extreme heat and pressure conditions within the Earth. This metamorphism alters their chemical composition and physical properties. Additionally, fossils are impressions or remains of ancient life forms that have been preserved in rock, providing a window into the past, and can often be discovered in areas like the Nevada desert.
Soil is the Earth's uppermost layer, composed of a mixture of clay, rock particles, and organic matter. It provides a nutrient-rich environment for plant growth, as seen in the fertile soil of the Amazon rainforest. Some rocks are porous, meaning they have spaces within them that allow water to pass through; sandstone is a prime example of such a rock. Weathering refers to the natural process by which rocks and minerals are broken down into smaller pieces, a process that can occur through physical or chemical means and may take millennia. Minerals, the solid chemical constituents found in rocks, contribute to the composition of various rock types, with granite in Russia noted for its high mineral content. Minerals can form crystals, which possess distinct geometric shapes, such as the cubic structure of salt crystals. The texture of a substance, such as the smooth feel of obsidian, is another characteristic used to describe rocks. Hardness is a measure of a substance's resistance to being reshaped, assessed by tools like the Mohs scale. Lastly, drainage is a property describing how well water can move through a material, with sandy soils typically offering better drainage than those composed mainly of clay.