Vocabulary - Multiplication and Division
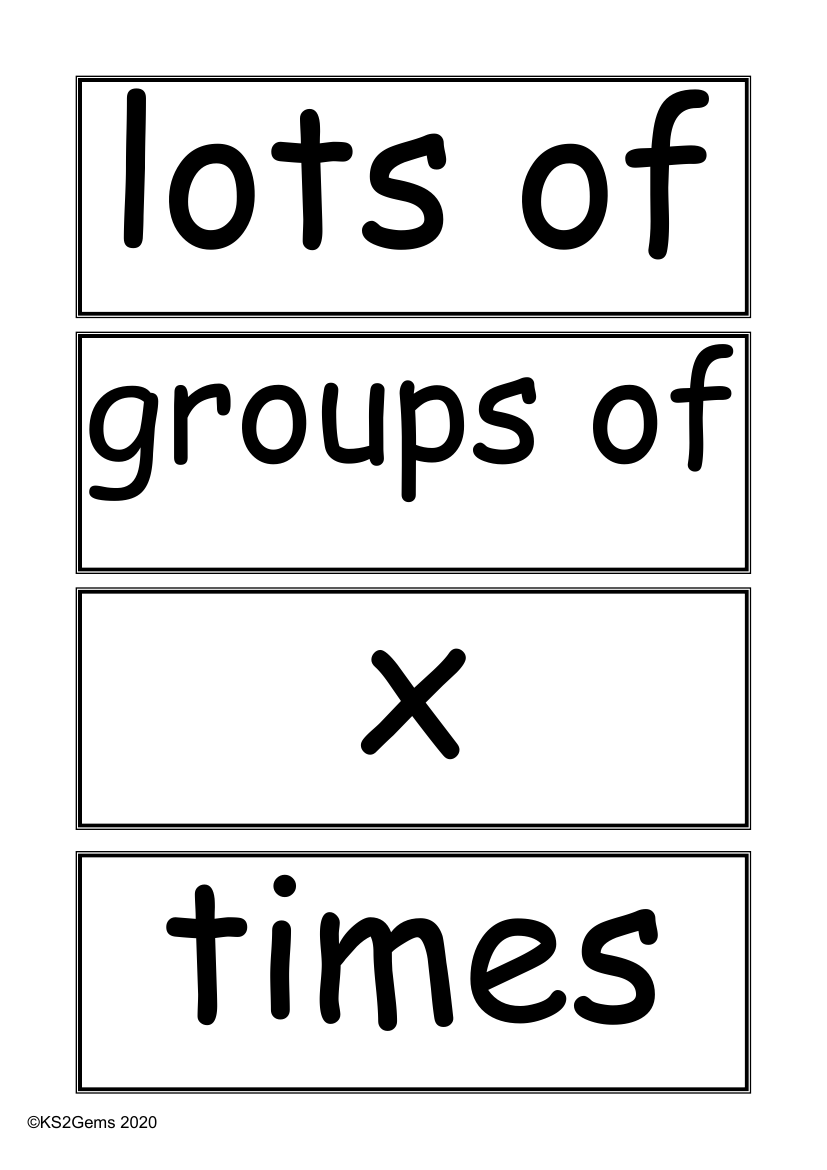
Maths Resource Description
The vocabulary related to multiplication and division is fundamental for students in KS2 to master mathematical concepts. Terms such as "lots of" and "groups of" are used to describe quantities that are to be multiplied. The symbol 'x' stands for 'times', indicating multiplication. Students learn to "multiply" and understand "multiplication" as an operation where one number is "multiplied by" another. A "multiple of" a number is the result of multiplying that number by an integer. The "product" is the result of multiplication, and phrases like "find the product," "once," "twice," and so on, up to "twelve times," are used to describe repeated addition of a number.
In the context of multiplication and division, an "array" is a visual representation using rows and columns, while to "double" means to multiply by two. Conversely, to "halve" is to divide by two. The concept of "sharing" or "sharing equally" is used to illustrate division, where a quantity is divided into smaller, equal parts, such as "one each" or "two each." Division can also be represented by grouping numbers in pairs, threes, or any equal group size, using the division sign '÷'. "Divided by" and "division" refer to the act of dividing, while "left over" and "remainder" describe what is left after division. The "equals" sign '=' signifies that two quantities are the same, and "factor" relates to numbers that can be multiplied to get a product. "Quotient" is the result of division, and "divisible by" indicates that a number can be divided by another without a remainder. "Inverse operation" is a term used to describe the opposite mathematical process, such as multiplication being the inverse of division. Lastly, terms like "scale up," "scale down," and properties such as "commutative," "associative," and "distributive" relate to advanced multiplication and division concepts, while "factor pairs," "dividend," and "divisor" are terms associated with division calculations.