Solve problems involving the calculation and conversion of units of measure 2 - Reasoning
Maths Resource Description
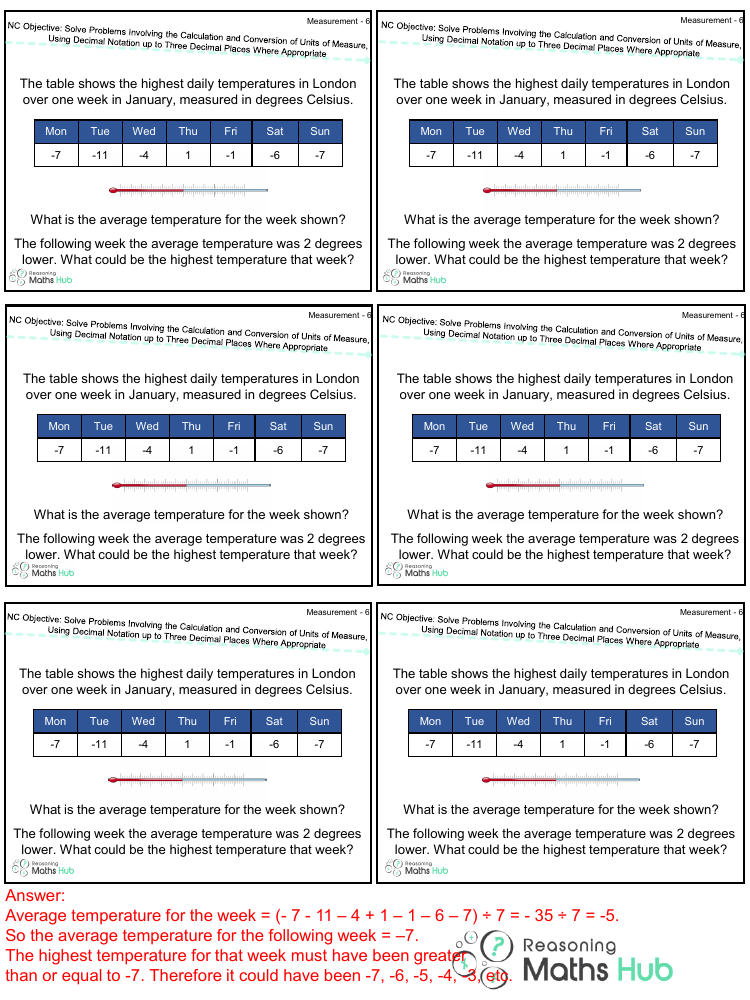
The task involves analysing a set of data on the highest daily temperatures in London over a week in January, with the temperatures provided in degrees Celsius for each day of the week. The data are as follows: Monday -7°C, Tuesday -11°C, Wednesday -4°C, Thursday 1°C, Friday -1°C, Saturday -6°C, and Sunday -7°C. To determine the average temperature for the week, one must sum the daily temperatures and divide by the total number of days, which is seven. The calculation is as follows: (-7 - 11 - 4 + 1 - 1 - 6 - 7) ÷ 7, which equals -35 ÷ 7, resulting in an average temperature of -5°C for the week.
For the subsequent week, the average temperature was reported to be 2 degrees lower than the previous week, making it -7°C. When considering what the highest temperature for that week could be, it is understood that it must be greater than or equal to the average temperature of -7°C. Therefore, the highest temperature for that week could be -7°C or any value above it, such as -6°C, -5°C, -4°C, -3°C, and so on. This reasoning is based on the fact that the average is a midpoint, and the highest temperature must be at least as high as the average or higher to maintain the calculated average temperature for the week.
