Multiplication and division - Vocabulary
Maths Resource Description
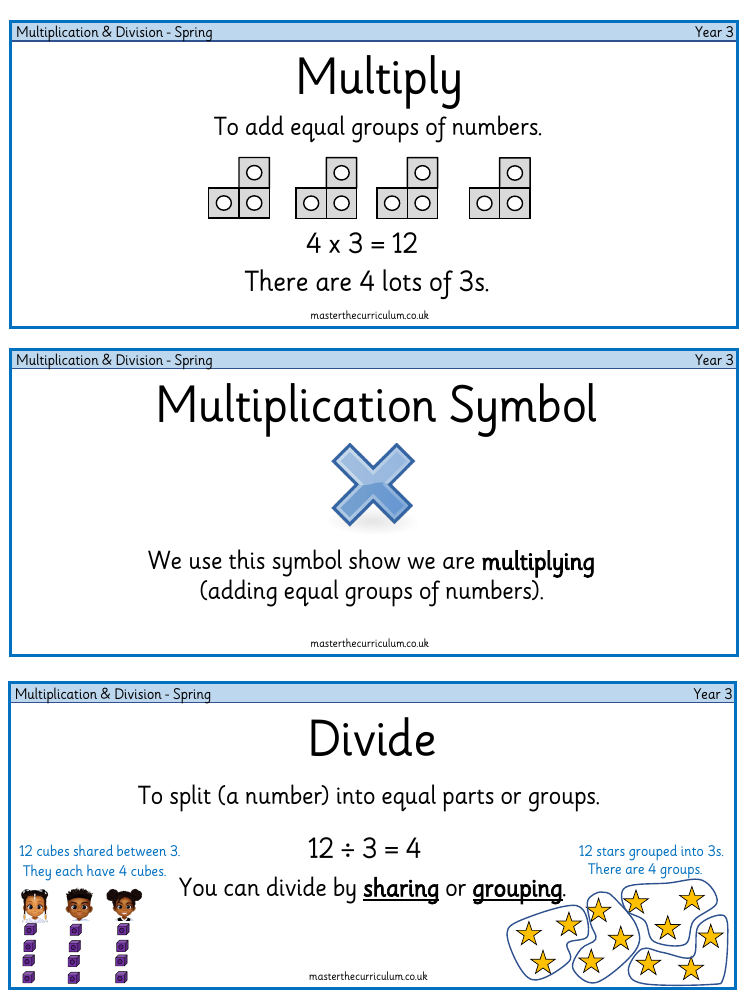
The fundamental concepts of multiplication and division are introduced to Year 3 students through a variety of terms and operations. Multiplication involves adding equal groups of numbers together, symbolised by the '×' sign. For example, '4 × 3 = 12' means there are four groups of three. Division, represented by the '÷' sign, is the process of splitting a number into equal parts or groups, such as '12 ÷ 3 = 4', which can be illustrated by dividing twelve stars into three equal groups or sharing twelve cubes between three people, with each person receiving four cubes.
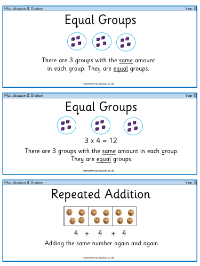
Students also learn about the concept of equal groups, where a quantity is divided into several groups with the same number of items in each. The term 'repeated addition' is used to describe the process of adding the same number multiple times, which is a fundamental principle of multiplication. Arrays, which are objects arranged in rows and columns, serve as visual aids to help children understand multiplication. They are introduced to the 'Commutative Law', which states that the order of numbers in multiplication does not affect the result, and the 'Distributive Law', which allows for breaking down a multiplication problem into simpler parts. Other key terms include 'multiplicand' (the number being multiplied), 'multiplier' (the number by which you multiply), and 'product' (the result of multiplication). Additional concepts such as 'scaling', 'partitioning', 'tens and ones', 'compare', 'inequality symbols', 'related facts', 'exchange', and 'remainder' are also part of the curriculum, enriching the students' understanding of multiplication and division.