States of Matter - Answers
Science Resource Description
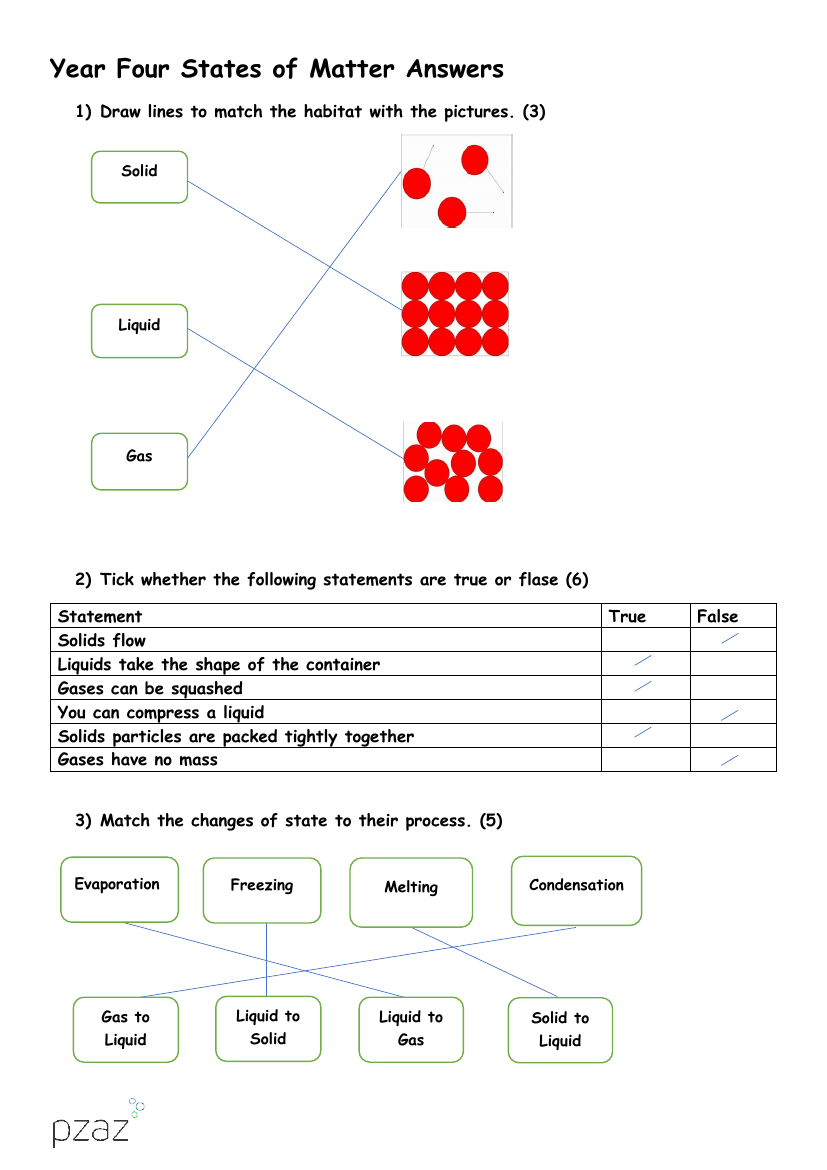
The answer sheet for Year Four's 'States of Matter' topic provides key responses to various questions on the subject. In the first question, students are expected to match different habitats with their corresponding pictures. The second question involves a true or false assessment where students must identify accurate statements about the properties of solids, liquids, and gases. For instance, the correct answers would acknowledge that liquids take the shape of their container and that solid particles are packed tightly together, while solids do not flow, gases can be compressed, liquids cannot be compressed, and gases do indeed have mass.
The third question requires students to match changes of state with their respective processes, such as freezing, melting, evaporation, and condensation. The melting point is identified as the temperature at which a solid turns to a liquid, while the boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid becomes a gas. In a table provided, students determine the state of matter of various substances at room temperature, such as oxygen and hydrogen being gases, water and mercury being liquids, and iron being a solid. The water cycle, also accepted as the hydrologic or hydrological cycle, is named as the movement of water around the Earth. Evaporation is the stage where liquid water turns into water vapour, with the Sun being the power source for this entire cycle. Clouds are formed during the condensation stage, and two forms of precipitation include rain, sleet, snow, and hail.