Perimeter, Area and Volume - Area of a Triangle (1) - Planning
Maths Resource Description
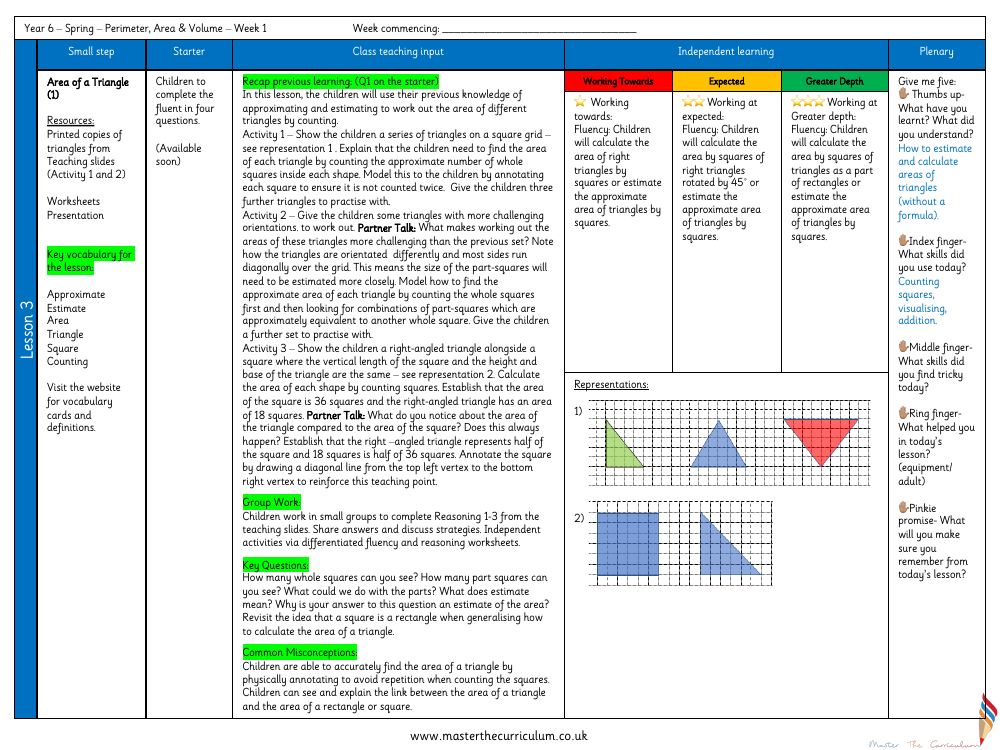
In a Year 6 classroom, pupils are introduced to the concept of measuring the area of triangles without relying on a preset formula. The lesson begins with a starter activity that prompts students to utilise their existing skills in approximation and estimation. The class is then presented with printed copies of various triangles on a square grid, as seen in the teaching slides. The initial task involves counting the number of whole squares within the triangles to determine the approximate area, with careful annotation to avoid double-counting. This hands-on approach is designed to cement the students' understanding of area measurement through visual and practical engagement.
The lesson progresses with more complex triangles that challenge the students' estimation skills due to their unconventional orientations on the grid. The children are encouraged to discuss the difficulties posed by these shapes and to estimate the areas by combining partial squares into whole ones. A key moment in the lesson is when the pupils compare the area of a right-angled triangle with that of a square, both of which share the same vertical length. Through counting and discussion, they discover that the triangle's area is precisely half that of the square. This discovery is reinforced by dividing the square with a diagonal line. The lesson concludes with group work and independent activities that cater to varying levels of understanding, from working towards fluency to achieving greater depth. Reflection activities encourage students to articulate what they've learned, the skills they've applied, and the strategies that have aided their learning process.