Multiplication and Division (1) - Vocabulary
Maths Resource Description
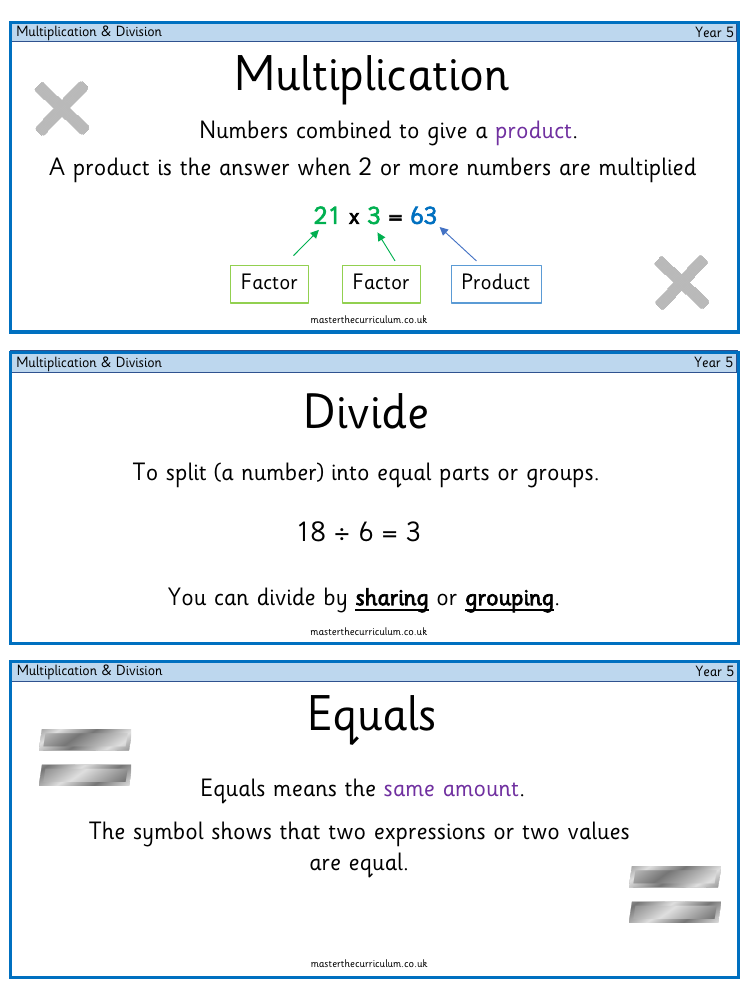
In the realm of mathematics for Year 5, the concept of multiplication is introduced as the process of combining numbers to yield a product, which is the result when two or more numbers are multiplied. For example, multiplying 21 by 3 gives a product of 63. This process involves factors—the numbers being multiplied—and can be visualised using arrays, which arrange objects in rows and columns to facilitate understanding. The multiplication symbol, often denoted by 'x', signifies that the numbers are to be multiplied. The commutative law states that the order of multiplication does not affect the product; therefore, 7 x 8 is the same as 8 x 7, both giving a product of 56.
Conversely, division is the act of splitting a number into equal parts or groups, such as dividing 18 by 6 to get 3. This can be done through sharing or grouping, as illustrated by sharing 21 cakes equally among 3 plates or determining how many jars are needed to store 21 marbles given that each jar fits 3. Division facts are linked to times tables and can be checked using the inverse operation, where multiplication and division are used to confirm the accuracy of calculations. For instance, the inverse of 3 x 6 = 18 is 18 ÷ 6 = 3. To aid in understanding these concepts, concrete methods using physical objects and pictorial methods like bar models and number lines can be employed. Additionally, the curriculum covers the use of area models and long multiplication for larger numbers, introducing students to the concept of integers—whole numbers without fractions or decimals.