Compare and sort common 2d and 3d shapes and everyday objects 4 - Reasoning
Maths Resource Description
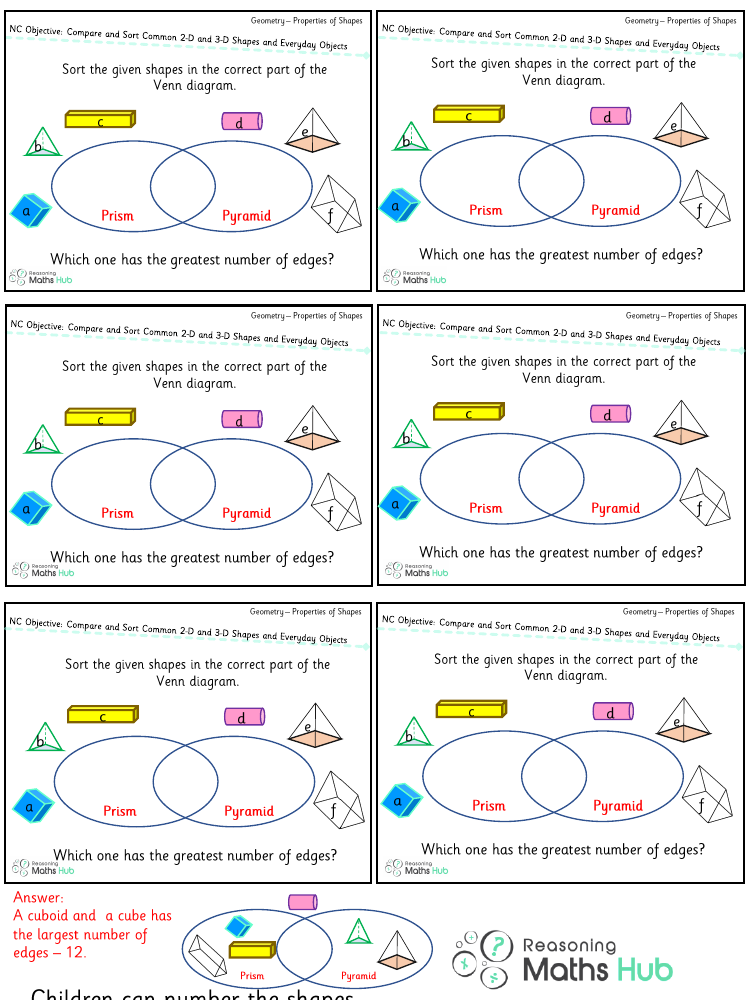
Comparing and sorting common 2D and 3D shapes, as well as everyday objects, is a critical skill in developing geometric understanding. When engaging in reasoning activities related to this topic, students are encouraged to look beyond the superficial attributes of shapes and consider their defining properties. For 2D shapes, this may involve examining the number of sides, length of sides, types of angles, and lines of symmetry. For 3D shapes, students would consider attributes such as faces, edges, vertices, and the shape of the faces themselves. Everyday objects can be compared and sorted based on the shapes they resemble, such as a cereal box resembling a rectangular prism or a ball resembling a sphere.
In a reasoning activity, students may be tasked with justifying their sorting criteria, providing opportunities to articulate their understanding of shape properties. For instance, they might compare a square to a rectangle, noting that while both have four sides, a square has all sides of equal length and four right angles, distinguishing it from a rectangle which only requires opposite sides to be equal. When sorting, they might group objects like cans, balls, and dice based on whether they are primarily composed of curved surfaces, like a cylinder or sphere, or flat surfaces, like a cube. Through these reasoning exercises, students develop a deeper comprehension of geometric concepts and enhance their ability to classify shapes and objects in the world around them.
