Place Value Decimals - PowerPoint
Maths Resource Description
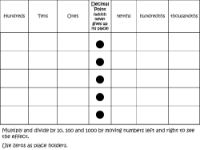
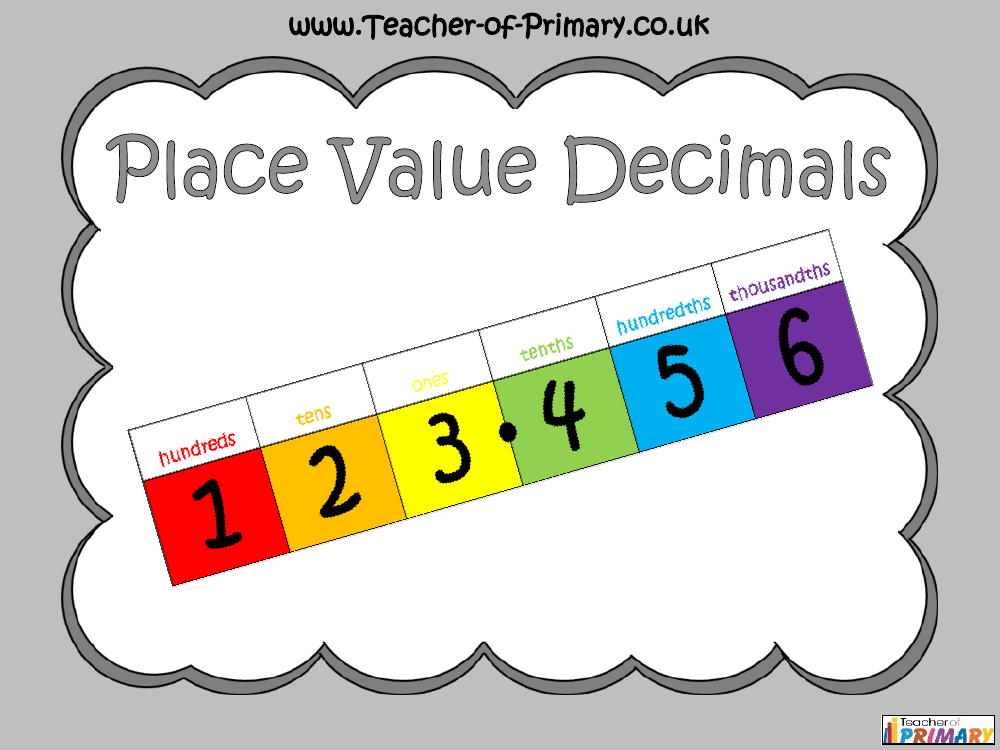
Understanding place value is crucial when working with decimal numbers. Each digit in a number has a specific value depending on its position or column. For instance, when a number has digits after the decimal point, these represent decimal fractions. The columns are named tenths, hundredths, and thousandths, indicating the fractional part of a whole number that each digit represents. A whole number can be divided into ten equal parts (tenths), a hundred equal parts (hundredths), and the pattern continues with each decimal place representing increasingly smaller divisions of the whole.
Decimals are essentially another way of expressing fractions; they denote equal parts of a whole number but are written differently. The decimal point plays a critical role in separating whole numbers from the decimal fractions. For example, if a shape is divided into ten parts and four are coloured, the fraction is 4/10, which is equivalent to 0.4 in decimal form. This concept extends to hundreds and thousandths as well, with each place value to the right of the decimal point representing a smaller unit. The lesson includes activities that help students convert fractions to decimals, compare decimal numbers, and understand how to order them correctly by using place value knowledge.