Add multiples of 10 to a 2-digit number
Maths Resource Description
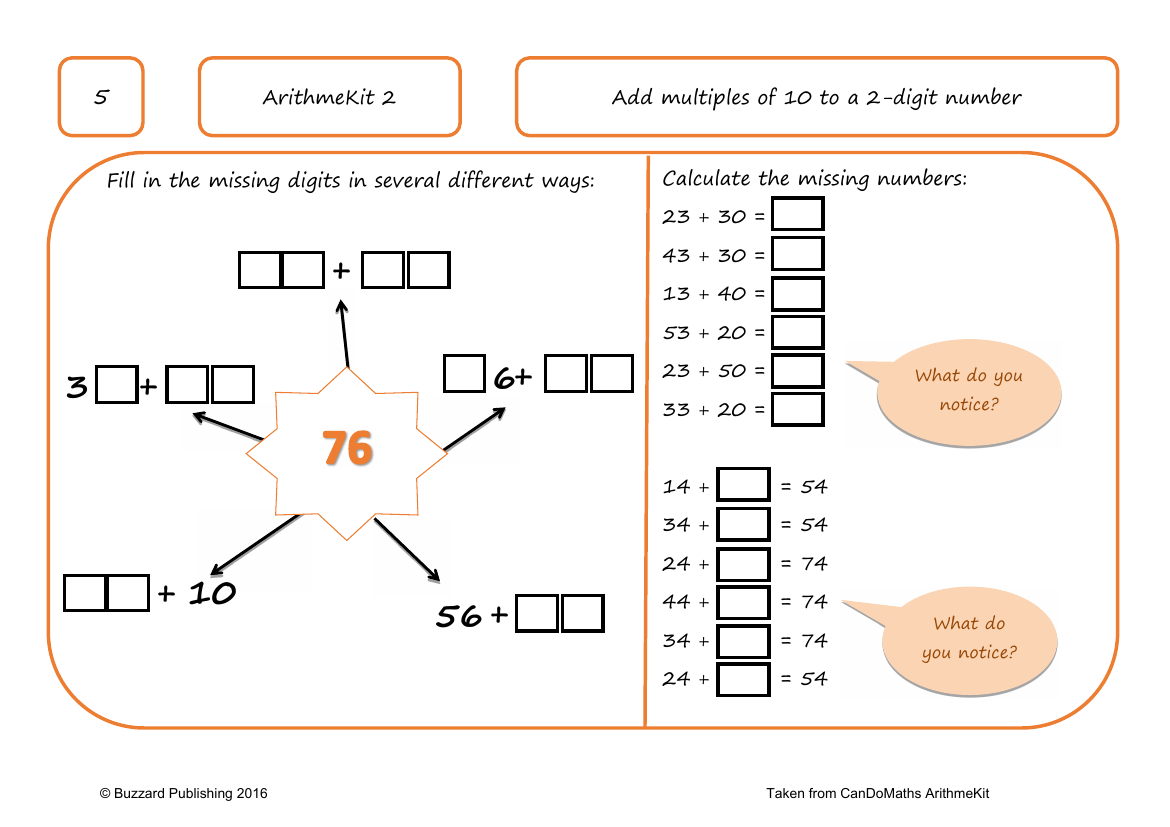
Exploring the addition of multiples of 10 to a 2-digit number offers a fundamental arithmetic skill for students. In this exercise, students are prompted to notice patterns and fill in missing digits to complete sums accurately. For example, when adding 3 and 6 to the number 56 with a multiple of 10, the missing figure in the sum can vary. Calculations such as 23 plus 30 equals 53, and 43 plus 30 equals 73, help students recognise that adding multiples of 10 increases the tens digit of the original number while the units digit remains unchanged. This pattern continues with other sums like 13 plus 40 equals 53 and 53 plus 20 equals 73, reinforcing the concept that the tens digit increases by the multiple of 10 added.
The exercise also challenges students to agree or disagree with Colin's statement that adding 40 to a 2-digit number results in the tens digit increasing by 4. This is indeed true, and students can use a number line or concrete resources to validate this. They are encouraged to solve problems with missing digits, such as finding the number that, when added to 14, results in 54, which would be 40. The activity extends to creating their own missing digit problems and solving them with the digits 0 to 9, used only once each. By engaging in these tasks, students develop their understanding of addition with multiples of 10 and enhance their problem-solving skills.
