Match up - Bones
Science Resource Description
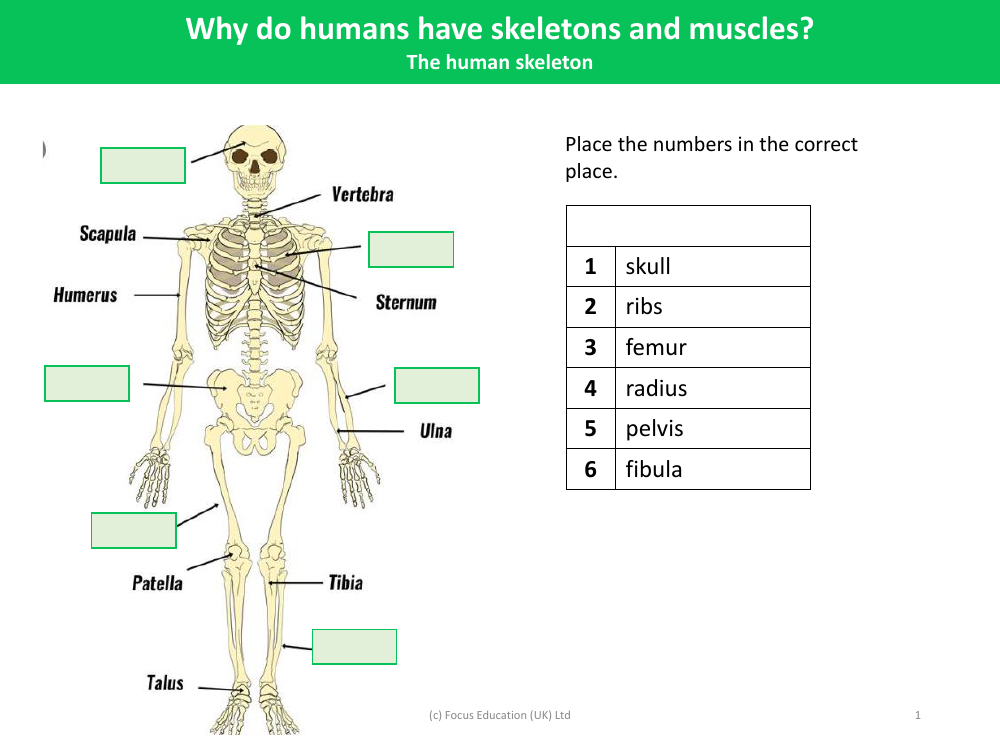
The human skeleton is a remarkable structure that serves several crucial functions for the body. It provides a rigid framework that supports the soft tissues of the body and protects vital organs. For instance, the skull, labelled as '1', encases and safeguards the brain, while the ribs, marked as '2', form a protective cage around the heart and lungs. The skeleton also facilitates movement in conjunction with muscles; bones act as levers that muscles pull on to create motion. The femur, or '3', is the longest and strongest bone in the body, forming a key component of the leg that aids in supporting the weight of the body and enabling locomotion.
Other bones play equally important roles. The radius, '4', is one of the two long bones in the forearm, allowing for the rotation and manipulation of the wrist and hand. The pelvis, '5', comprises a basin-shaped structure of bones that connects the spine to the lower limbs, providing a strong foundation for the torso and a site for muscle attachment. Lastly, the fibula, '6', is a slender bone located in the lower leg that stabilizes the ankle and supports the muscles of the lower leg. Together, these bones make up just a part of the complex and intricate skeletal system that underpins human anatomy and physiology.