What are the main differences between carnivore, omnivore and herbivore? - Presentation
Science Resource Description
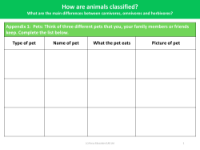
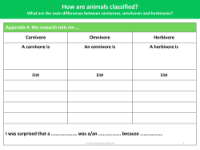
The primary distinctions between carnivores, omnivores, and herbivores lie in their dietary habits, which are a fundamental part of the science curriculum for Key Stage 1 pupils. Carnivores are animals that exclusively consume meat, deriving their nutrition from preying on other animals. Herbivores, on the other hand, feed solely on plant material. Omnivores have the most varied diet, as they consume both plants and meat. This classification is crucial for understanding the diversity of animal diets and how they interact with their ecosystems. The national curriculum requires that pupils identify and name common animals across various categories, including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, and classify them according to what they eat.
In addition to dietary classification, the curriculum also covers the structural differences among common animals. For example, amphibians typically begin life in water with gills and tails, exemplified by frogs and newts, while reptiles are cold-blooded, often lay eggs, and have skin covered with hard, dry scales. Mammals are warm-blooded, breathe air, and have a backbone. Knowledge organisers and activities within the curriculum help students to sort animals into categories, understand the characteristics that define mammals, reptiles, and amphibians, and recognise the differences between living, non-living, and never alive entities. They also encourage students to research animals in specific habitats and to group or classify them according to their diets, thereby deepening their understanding of biological classification.