Separation by Evaporation - Teacher Explanation

Science Resource Description
Welcome to lesson 5.10, 'Separation by Evaporation', part of the Year 5 curriculum on properties and changes of materials. In this lesson, pupils will apply their understanding of solids, liquids, and gases to explore various separation techniques, focusing particularly on evaporation. Health and safety are paramount, with specific instructions to wear safety goggles, stand up (with chairs on desks), tie back long hair, and ensure clear walkways to avoid accidents. The lesson involves handling liquids, which can be slip hazards, and the use of tea lights, for which only teachers should manage the lighter. Pupils are advised to let heated equipment cool before disassembly. The lesson also provides opportunities for cross-curricular links, such as researching the drying of laundry for understanding evaporation and performing calculations with the results, integrating mathematics into the science experiment.
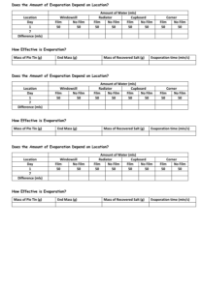
The practical component of the lesson involves two experiments. The first one demonstrates water evaporation by measuring water in cups, marking the level, and observing the changes over a week in different classroom locations. Pupils will notice that water levels in open cups decrease due to evaporation, while those covered with cling film show negligible evaporation but some condensation. The second experiment investigates the separation of a solute (salt) from a solvent (water) through evaporation. Using a white tile or plate, measuring cylinder, spoon, tea light candles, foil pie tins, tea light holder, stopwatch, lighter, scales, salt, and water, pupils will create a salt solution and observe evaporation caused by the heat from a tea light. They will learn that while the water evaporates, the salt remains, demonstrating an effective separation technique. Pupils will record the time taken for evaporation and the final weight of the salt, learning the scientific principle of evaporation as a transition from liquid to gas and its practical applications in separating solutes from solvents.