Pulmonary and Systemic circuits - Worksheet
Science Resource Description
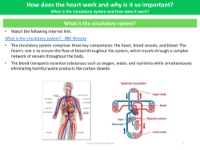
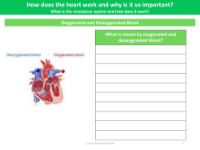
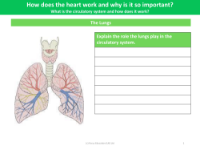
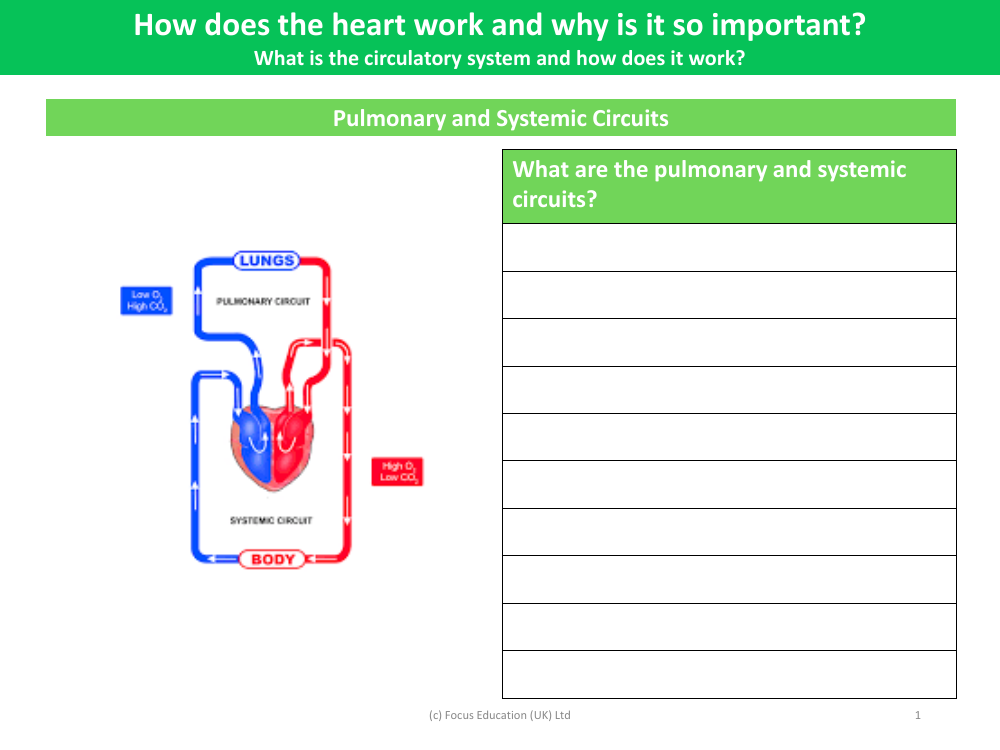
The worksheet on Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits seeks to educate students on the two main pathways through which blood travels in the human body. The pulmonary circuit is responsible for transporting deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it releases carbon dioxide and absorbs oxygen. In contrast, the systemic circuit carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body, delivering vital oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs before returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Understanding these circuits is crucial as they are integral components of the circulatory system, which maintains the vital functions of the body.
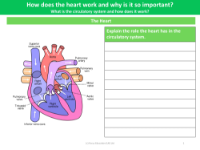
Additionally, the worksheet prompts learners to explore the workings of the heart and its significance in the circulatory system. The heart is a powerful muscular organ that acts as a pump to propel blood through the pulmonary and systemic circuits. By rhythmically contracting and relaxing, the heart ensures a continual flow of blood, which is essential for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and waste products to and from body cells. Students are encouraged to delve into the structure and function of the circulatory system, learning how this complex network of vessels and chambers works in harmony to sustain life.