Vocabulary - Number and number sequences
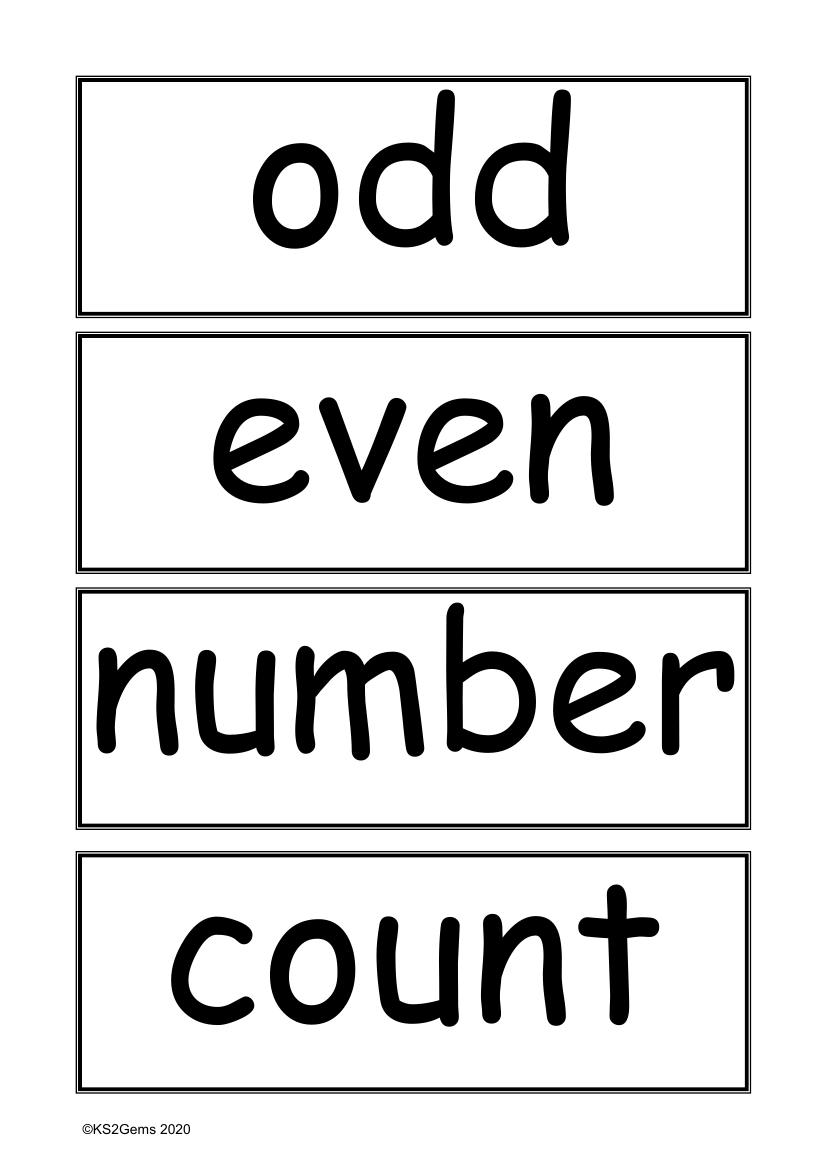
Maths Resource Description
The vocabulary set provided by KS2Gems in 2020 encompasses a range of terms related to numbers and number sequences, vital for Key Stage 2 mathematics. The terms 'odd' and 'even' refer to the two categories of integers, with odd numbers being those that cannot be divided evenly by two, and even numbers being those that can. The word 'number' is a fundamental concept, representing a mathematical value used in counting and measuring, while 'count' refers to the action of determining the total number of items in a set. 'How many?' and 'how many times?' are questions that encourage students to think about quantity and frequency, respectively.
Further terms such as 'multiple of' relate to numbers that can be divided by another number without a remainder, while 'digit' refers to any of the numerals from 0 to 9, the building blocks of larger numbers. 'Consecutive' describes numbers that follow one after the other in order, and 'sequence' is a set of numbers arranged in a specific pattern. Students are encouraged to 'continue' patterns, 'predict' future numbers in a sequence, and identify 'pairs' or sets of two. Understanding the 'rule' or 'relationship' in number sequences helps students to 'sort' and 'classify' numbers according to their properties.
Mathematical properties such as 'divisibility'—whether a number can be divided evenly by another—and related terms like 'divisible by' and 'factor' are key concepts. A 'square number' is the product of a number multiplied by itself, while to 'factorise' means to break down a number into its constituent factors. 'Prime number' refers to a number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. 'Prime factor' is a factor that is a prime number, and 'cube number' and 'triangular number' refer to numbers that are the result of cubing an integer and the sum of natural numbers up to a certain point, respectively.
Additional terms include 'cardinal number', which signifies the size of a set, and 'ordinal number', which indicates position within a sequence. The term 'inequality' is used to describe the relationship between two values that are not equal, and 'place holder' signifies the positional value of a digit in a number. 'Interval' refers to the difference between two numbers, and 'natural number' is another term for a positive integer, typically used in counting. These terms are crucial in developing a student's understanding of numbers and their relationships, as they progress through Key Stage 2 mathematics.