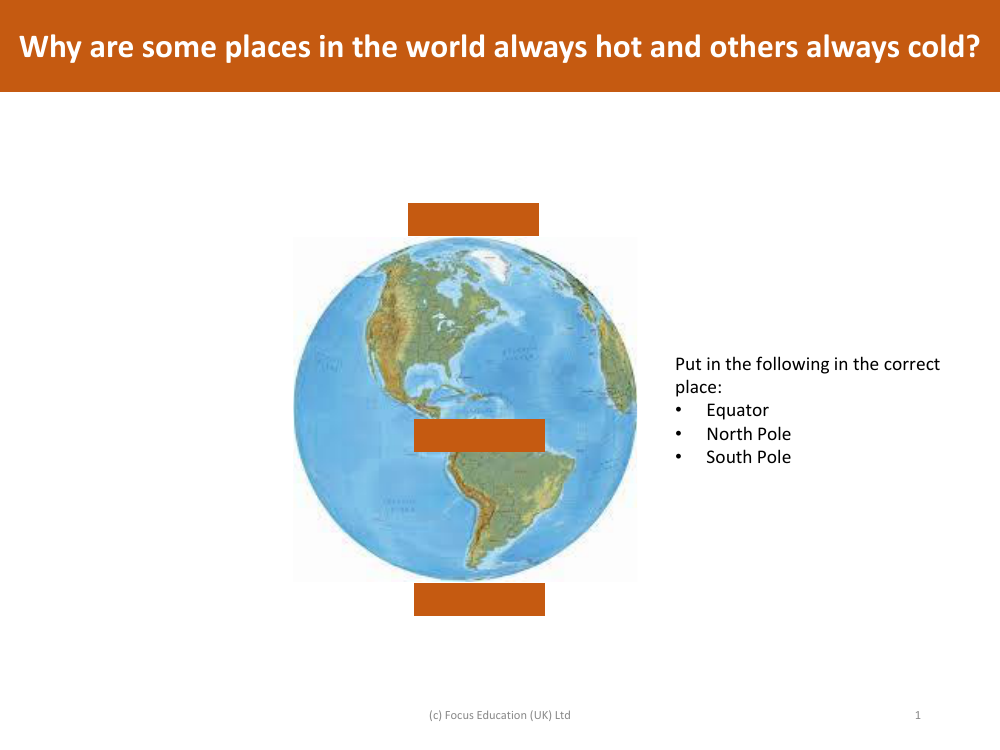
Picture match - Equator, South Pole and North Pole
Geography Resource Description
In a geography lesson aimed at helping students understand the Earth's geography and climate, a picture match activity is used to correctly identify and place the Equator, the North Pole, and the South Pole on a map or globe. The Equator is an imaginary line that circles the globe horizontally at its widest point and is located equidistant from the poles; it should be placed at the midpoint between the North and South Poles. The North Pole is at the very top of the Earth, representing the northernmost point, while the South Pole is at the bottom, representing the southernmost point.
The variation in temperature across different parts of the world is explained by the Earth's tilt and its orbit around the Sun. The Equator receives direct sunlight year-round, making the climate consistently warm due to the concentrated solar radiation. In contrast, the North and South Poles are tilted away from direct sunlight, receiving less concentrated solar energy, which results in colder temperatures. Additionally, during their respective winter months, each pole experiences a prolonged period of darkness known as polar night, contributing to the extreme cold. This fundamental understanding of the Earth's axial tilt and its impact on climate is essential for students learning about global geography and meteorology.