How can we classify solids, liquids and gasses? - Presentation
Science Resource Description
In a Year 4 science curriculum, students are taught to differentiate and group materials based on their states: solids, liquids, and gases. They explore how certain materials can transition between these states when subjected to heating or cooling, and they learn to measure or research the temperature at which these changes occur in degrees Celsius (°C). The curriculum also covers the processes of evaporation and condensation, particularly in the context of the water cycle, and students are encouraged to link evaporation rates to temperature changes. Through this, they gain substantive knowledge about the state changes of various materials, including water, and learn the specific temperatures at which water boils and freezes.
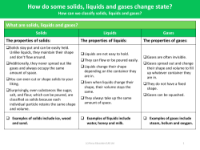
The instructional content further delves into the properties that define solids, liquids, and gases. Solids are described as maintaining a consistent shape and volume, liquids as having a fixed volume but taking the shape of their containers, and gases as being able to spread out and fill any given space without a fixed shape or volume. Pupils are introduced to key vocabulary such as evaporation, condensation, melting, and solidifying, and are taught the importance of these terms in understanding the water cycle and the state changes of matter. The lessons build on prior knowledge from earlier years and are designed to prepare students for more advanced concepts in Year 5, such as reversible and irreversible changes.