Changes of State - Boiling and Melting Points
Science Resource Description
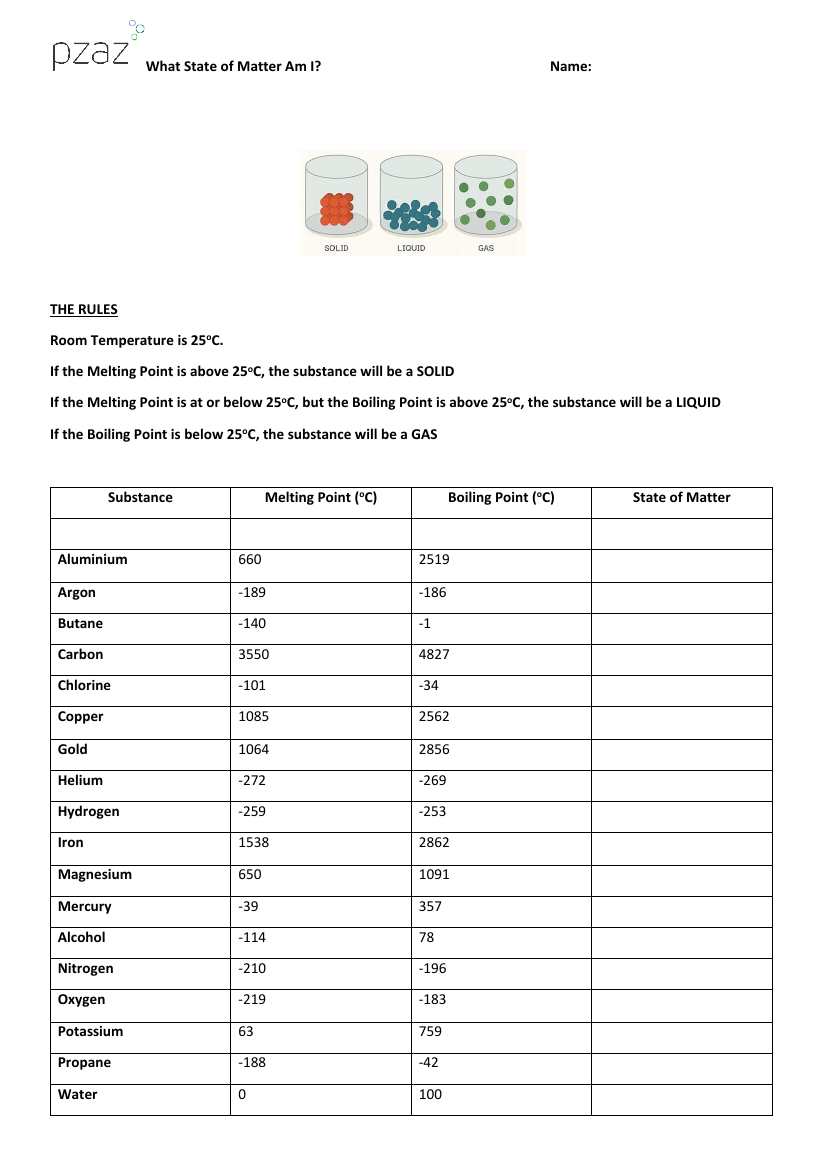
The educational activity "What State of Matter Am I?" is designed to help students understand the states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas—based on the melting and boiling points of various substances. The rules are straightforward and use room temperature, set at 25°C, as the benchmark for determining the state of a substance. If a substance's melting point is above 25°C, it will be in a solid state at room temperature. Conversely, if the melting point is at or below 25°C, but the boiling point is above 25°C, the substance is considered a liquid. Finally, if the boiling point is below 25°C, the substance exists as a gas at room temperature.
Using these rules, students can determine the state of matter for a list of substances by examining their respective melting and boiling points. For example, Aluminium, with a melting point of 660°C and a boiling point of 2519°C, is a solid at room temperature. Argon, on the other hand, has a melting point of -189°C and a boiling point of -186°C, making it a gas. Similarly, Mercury, with a melting point of -39°C and a boiling point of 357°C, is a liquid at room temperature. This activity not only reinforces the concept of states of matter but also familiarises students with the physical properties of common elements and compounds, such as Iron, Gold, and Water.