Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division - Long division - 3-digits by 2-digits (no remainders) - Presentation

Maths Resource Description
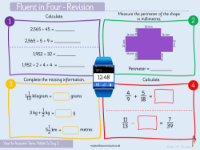
Lesson 15 delves into the method of long division, specifically focusing on dividing three-digit numbers by two-digit numbers without remainders. This lesson is designed to enhance students' understanding of key division concepts and terminology such as quotient, divisor, and dividend. For example, in the division equation 432 ÷ 12 = 36, students are encouraged to identify each part of the calculation. The lesson's activities guide students through the process of long division step by step, using multiples to aid in the division of two-digit numbers. The examples provided, such as 765 ÷ 17, 450 ÷ 15, and 702 ÷ 18, offer students the opportunity to apply their knowledge and practise the method of long division.
As part of the learning process, students are prompted to discuss why they subtract totals from the starting number, viewing division as repeated subtraction. This concept is reinforced through various exercises, including identifying the odd one out among division calculations and spotting any mistakes within given examples. The lesson also poses questions to encourage critical thinking, such as how multiples can be used in division and the significance of the arrow in long division, which represents the movement of the next digit coming down to be divided. Independent work tasks further challenge students to utilise the long division method, record helpful multiples, and articulate their reasoning behind identifying errors and odd calculations.