Multiplication and division - Vocabulary
Maths Resource Description
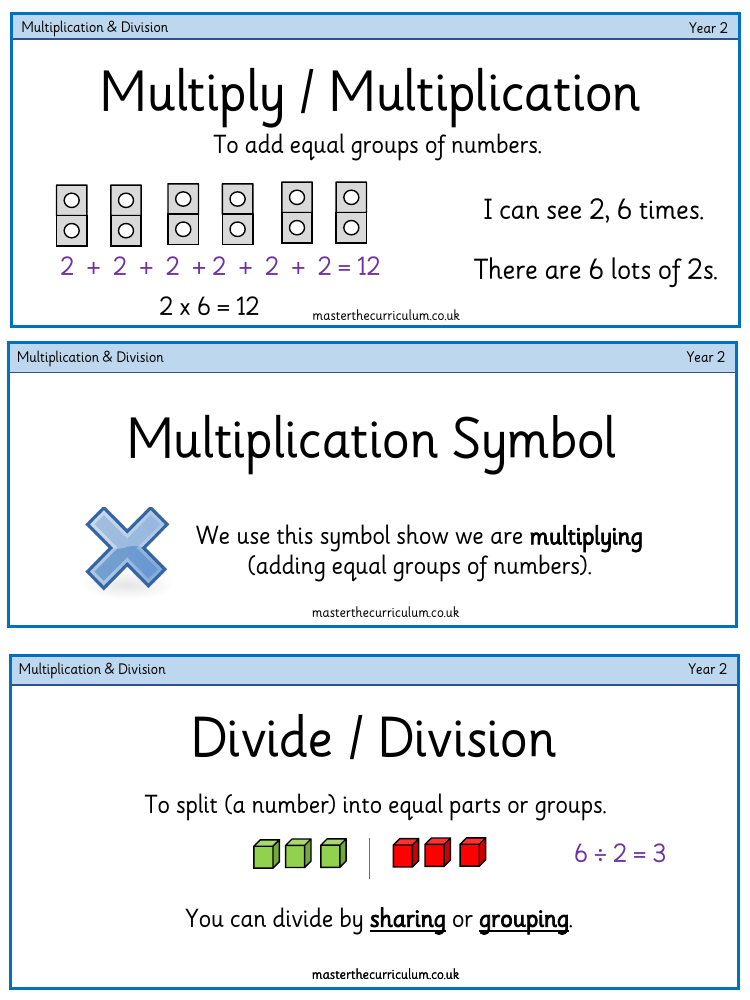
In Year 2, students are introduced to the fundamental concepts of multiplication and division. Multiplication is the process of adding equal groups of numbers together. For instance, the phrase "I can see 2, 6 times" translates to the multiplication sentence 2 x 6, which equals 12. This is the same as adding 2 six times (2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12). The multiplication symbol (×) is used to indicate that we are multiplying, or adding equal groups of numbers. Division, on the other hand, involves splitting a number into equal parts or groups. It can be done by sharing or grouping. For example, dividing 6 by 2 (6 ÷ 2) results in 3 because there are 3 equal groups of 2 in 6.
Understanding the concept of 'equal' is also crucial, as it refers to the same amount. When discussing division, the division symbol (÷) is employed to show that we are dividing into equal amounts, either by sharing or grouping. Repeated addition is another key concept, which means adding the same number over and over again, such as 5 added to itself five times (5 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5), which is equivalent to 5 x 5 and equals 25. Additionally, students learn about 'equal groups' where groups contain the same number of objects, and 'sharing', which involves dividing objects equally among recipients. 'Grouping' is finding how many equal groups can be made from a set of objects. Other important terms include 'halving', which is dividing equally into two parts, and 'doubles', which means having two of the same number or group. The curriculum also covers 'number sentences' that contain numbers and symbols, 'odd' and 'even' numbers, and recognising 'patterns' in ordered sets according to a rule. These foundational concepts are essential for building arithmetic skills in young learners.