Position and Direction - Vocabulary
Maths Resource Description
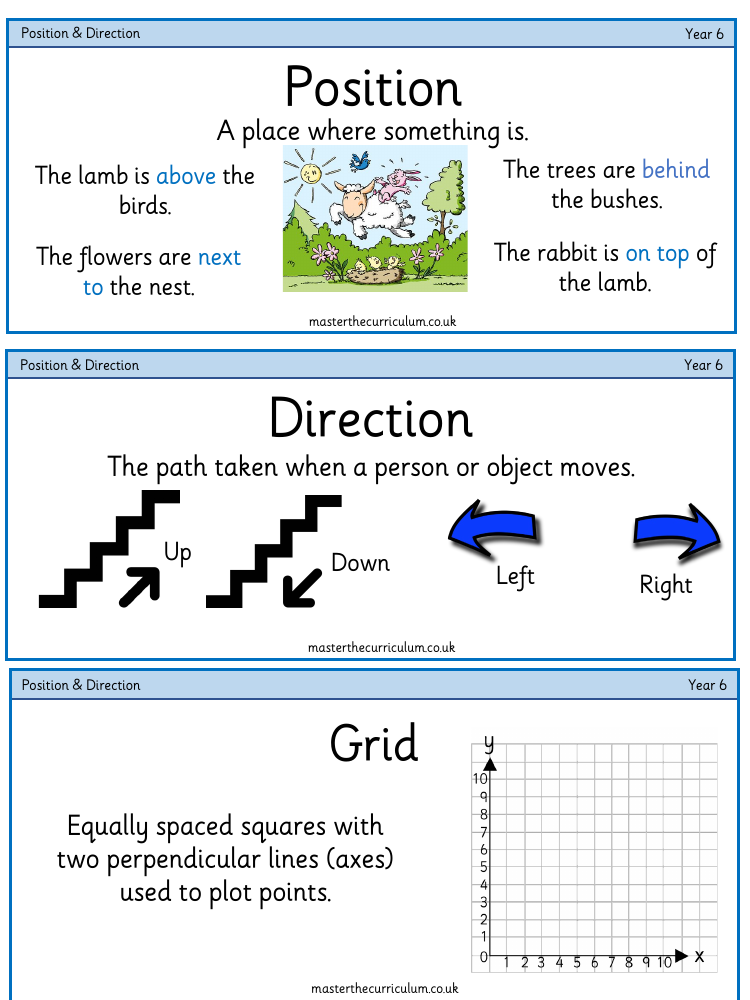
The Year 6 Position & Direction vocabulary encompasses a range of terms essential for understanding the basics of geometry and spatial awareness. 'Position' refers to the specific place where something is located, while 'Direction' is the path taken when moving from one point to another. A 'Grid' is a network of equally spaced squares formed by two perpendicular lines known as axes, which are used to plot points. 'Co-ordinates' are pairs of numbers indicating an exact position on this grid. The 'First Quadrant' is the section of the grid in the upper right corner where both x (horizontal axis) and y (vertical axis) values are positive.
The concept of 'Vertex' or 'Vertices' pertains to the point or points where two lines or edges meet, forming a 2D shape. When a grid extends to show negative scales, it reveals 'Four Quadrants', with 'Positive Co-ordinates' moving right on the x-axis and up on the y-axis, while 'Negative Co-ordinates' go left on the x-axis and down on the y-axis. The 'Origin' is where the x and y axes intersect, with co-ordinates (0,0). 'Congruent' shapes are identical in size and shape, and 'Orientation' refers to the direction in which an object is placed. 'Equidistant' points are the same distance from a central point, while 'Symmetry' implies that an object has identical forms on both sides of a line of symmetry. A 'Polygon' is a flat 2D shape with straight, fully closed sides. 'Translation' involves moving a shape on a grid without rotating or resizing it, and 'Reflection' is flipping a shape symmetrically across a mirror line, which can be 'Horizontal' or 'Vertical' relative to the x-axis and y-axis, respectively.