Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division - Mental calculations - Presentation

Maths Resource Description
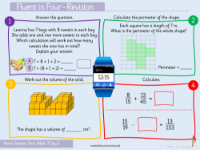
Lesson 25 focuses on enhancing students' proficiency with mental calculations, specifically on how to select the most efficient strategies for solving various mathematical operations. The term 'efficient mental strategy' refers to the quickest and simplest way to perform calculations in one's head. Students are encouraged to discuss and provide examples of such strategies. The lesson's activities challenge students to rearrange the order of operations in given calculations to facilitate mental computation. For example, changing the sequence of multiplications like 50 x 16 x 2 to 2 x 50 x 16 makes it easier to calculate mentally by taking advantage of the commutative property of multiplication.
Another aspect of the lesson involves practical application, where students are tasked with verifying transactions, such as determining whether Zach was overcharged for his shopping by quickly estimating the total cost of items and comparing it to the charged amount. This includes rounding prices to the nearest whole number to simplify mental addition. Additionally, the lesson covers strategies for estimating answers and understanding the usefulness of approximations in calculations. For example, estimating the value of 'B' when given 'A' and 'C' in various scenarios, and discussing the efficiency of different methods for subtraction, such as the column method versus using number bonds or adjusting numbers for easier calculation. Independent work reinforces these concepts, asking students to apply these strategies and discuss their reasoning behind the efficiency of different methods.