Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division - Multiply 4-digits by 1-digit (Pictorial representations) - Planning
Maths Resource Description
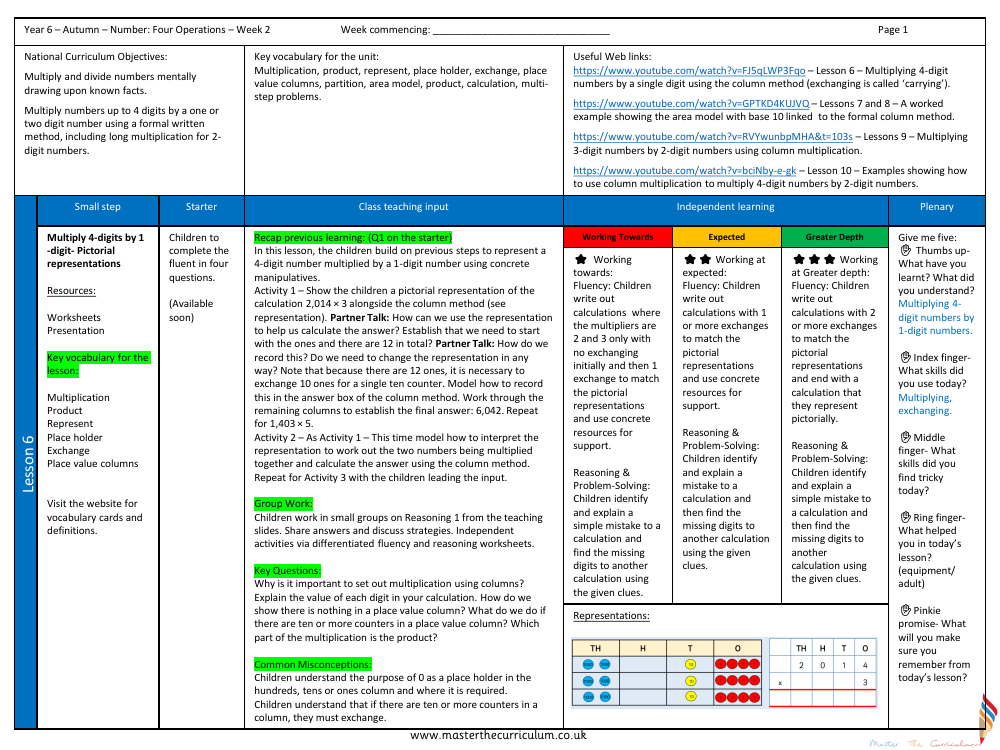
In a Year 6 mathematics lesson focusing on the four operations of arithmetic, students are introduced to the concept of multiplying 4-digit numbers by a single digit. The National Curriculum objectives for this lesson include multiplying and dividing numbers mentally, drawing upon known facts, and using formal written methods for multiplication, such as long multiplication for numbers with two digits. Key vocabulary terms such as 'multiplication', 'product', 'represent', 'place holder', 'exchange', and 'place value columns' are highlighted. Students are encouraged to use pictorial representations to understand and solve multiplication problems. Worksheets and presentations serve as resources, with vocabulary cards and definitions available to aid learning.
The lesson begins with a starter activity that prompts students to recall previous learning. They then progress to using concrete manipulatives and pictorial representations to visualise the multiplication process. For example, they might explore how to multiply 2,014 by 3 using a column method, discussing the importance of place value and the process of exchanging when more than ten counters accumulate in a single column. This hands-on approach is designed to deepen understanding and ensure that students can accurately record and calculate products. Group work and independent activities, differentiated by fluency and reasoning levels, allow students to practice and apply their knowledge, while plenary sessions offer opportunities to address common misconceptions and consolidate learning. The lesson aims to build confidence in multiplying 4-digit numbers by a single digit, emphasising the significance of exchanging and the use of zero as a place holder.



