Measurement Length and Perimeter - Vocabulary
Maths Resource Description
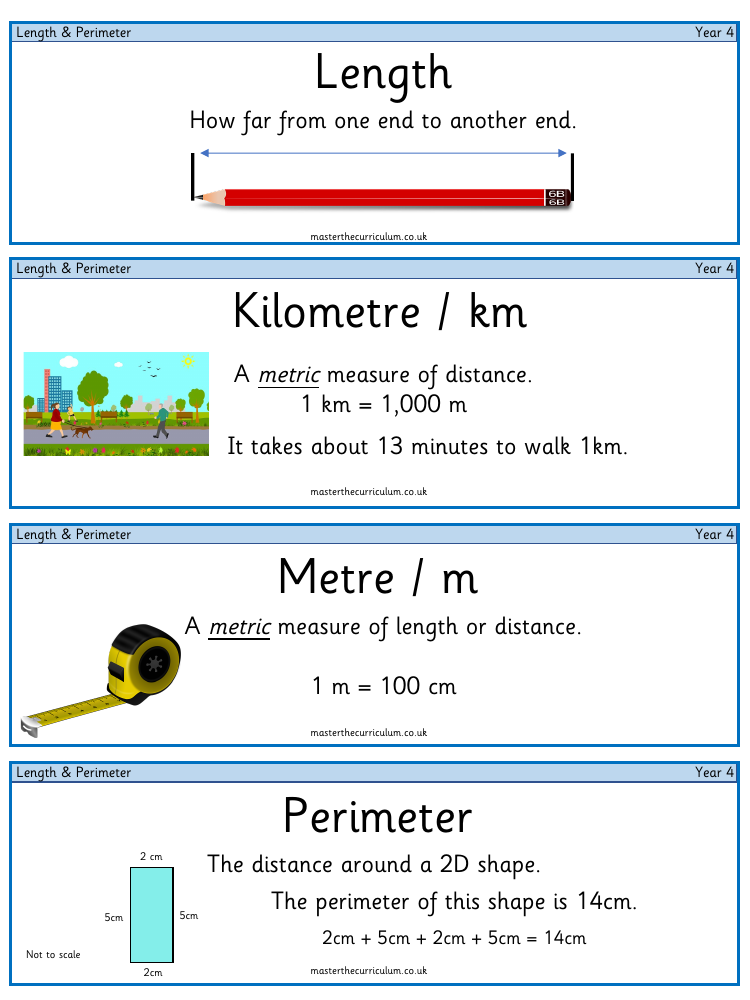
In the context of measurement, length refers to the extent from one end of an object to the other. It is commonly measured in metres (m), with one metre equating to 100 centimetres (cm). A larger unit of length is the kilometre (km), which is a metric measure of distance where 1 km equals 1,000 metres. These units help in quantifying how far apart two points are. For example, it is estimated that an average person can walk 1 km in about 13 minutes.
Perimeter, on the other hand, is the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape. To calculate the perimeter, one must add together the lengths of all the sides. For instance, if a rectangular shape has two sides measuring 2 cm and the other two measuring 5 cm, its perimeter would be the sum of all four sides, which in this case is 14 cm (2 cm + 5 cm + 2 cm + 5 cm). In geometry, a grid is a network of horizontal and vertical lines that intersect, often used to measure dimensions on a plane. A rectilinear figure is a polygon where all sides meet at right angles, and these figures consist entirely of straight lines. Width is a dimension that measures how wide a shape is, and in general, dimensions are measurements of length in a single direction. For example, a line has one dimension, a rectangle has two (width and height), and a cuboid has three (width, depth, and height).